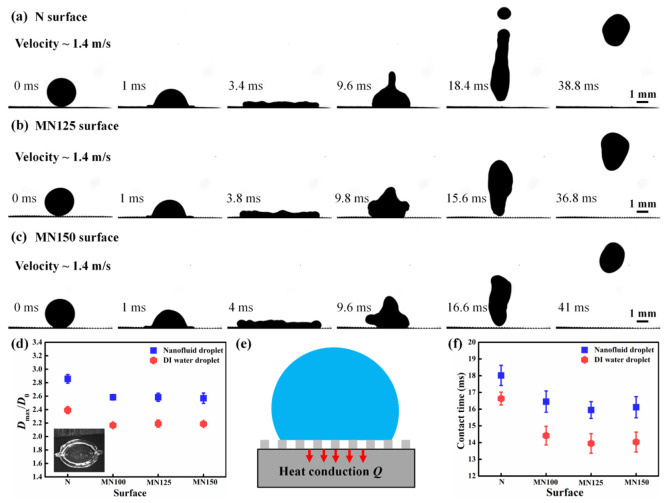
Figure 5.
(a) Selected snapshots of a nanofluid droplet impacting the cold N superhydrophobic Cu surface (−5 °C) at a velocity of 1.4 m/s. (b) Selected snapshots of a nanofluid droplet impacting the cold MN125 superhydrophobic Cu surface (−5 °C) at a velocity of 1.4 m/s. (c) Selected snapshots of a nanofluid droplet impacting the cold MN150 superhydrophobic Cu surface (−5 °C) at a velocity of 1.4 m/s. (d) Comparison of spreading ratio Dmax/D0 of the nanofluid droplet and the DI water droplet on the cold N, MN100, MN125, and MN150 superhydrophobic Cu surfaces (−5 °C) at a velocity of 1.4 m/s. (e) Schematic illustration of heat transfer from the nanofluid droplet to the cold Cu superhydrophobic surface. (f) Contact time of the nanofluid droplet and the DI water droplet on the cold N, MN100, MN125, and MN150 superhydrophobic Cu surfaces (−5 °C) at a velocity of 1.4 m/s.