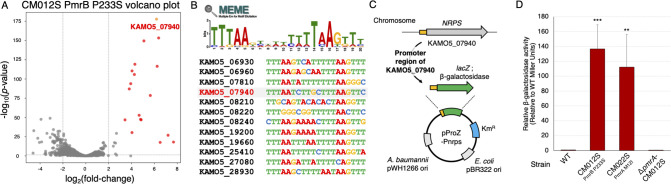
Fig 2.
Construction of the PmrAB reporter assay system for A. baumannii. RNA-seq analysis was conducted on the pmrB-activating mutant strain CM012S (P233S mutant), established from ATCC 19606 (WT strain). (A) A volcano plot comparing the CM012S strain with the WT strain is presented. The red dots (representing 17 genes) signify the PmrAB regulon. The gene KAMO5_07940, which is significantly upregulated [P value = 2.20 × 10−178, log2 (fold change) = 6.18], is highlighted with a yellow dot. (B) The 200-bp upstream region of the PmrAB regulon genes was extracted, and a consensus sequence predicted to bind PmrA was identified using the MEME Suite. (C) A schematic diagram of the reporter plasmid pProZ-Pnrps. Based on shuttle vectors for A. baumannii and E. coli, the lacZ gene encoding β-galactosidase was introduced downstream of the promoter region upstream of the KAMO5_07940 gene. (D) The pProZ-Pnrps plasmid was introduced into CM012S (pmrB mutation strain), CM022S (pmrA mutation strain), and pmrA disruption in pmrB-activating strain (pmrA-CM012S), and relative β-galactosidase activity was measured. Experiments were conducted independently in triplicate, and the results are presented as mean values with standard deviations represented by error bars. Statistical significance is shown as a reference of the WT strain mRNA levels using Dunnett’s test; ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01.