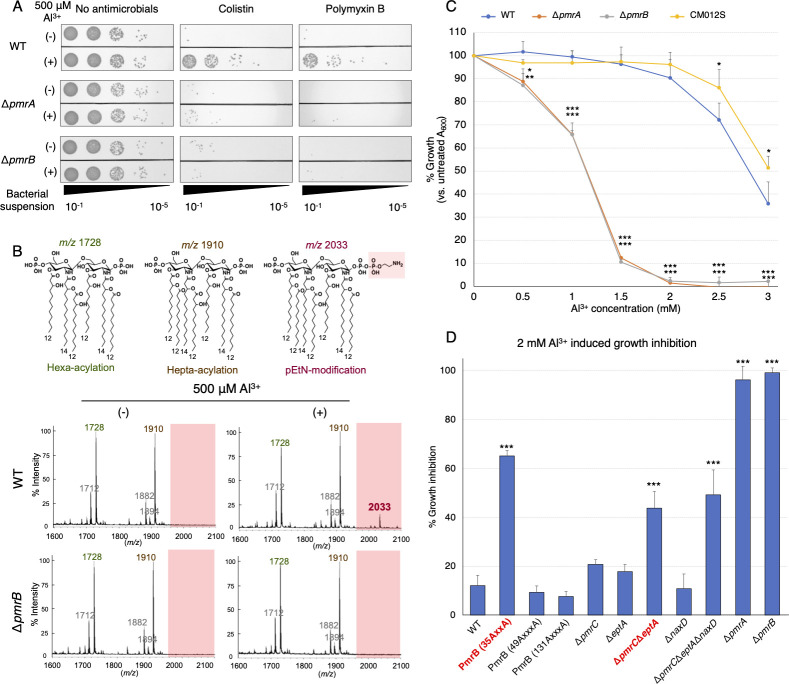
Fig 5.
A. baumannii PmrAB-dependent phenotypic changes induced by Al3+. (A) The ATCC 19606, ΔpmrA, and ΔpmrB strains in the logarithmic growth phase were exposed to 500 µM AlCl3 for 2 h. Subsequently, the bacterial suspension was adjusted to an OD600 of 0.2. After incubating the bacterial suspension with 10 µg/mL colistin or 7 µg/mL polymyxin B, or without any antimicrobial agent (control) for 2 h, 10 µL of a 10-fold serial dilution (ranging from 10−1 to 10−5) of the bacterial suspension was plated onto LB agar plates, which were then incubated at 37°C for 24 h. Experiments were conducted in triplicate, and images of representative agar plates are shown. (B)The ATCC 19606 (WT; middle row) and ΔpmrB strain (bottom row) in the logarithmic growth phase were exposed to 500 µM AlCl3 for 2 h. Lipid A was extracted from the bacteria, and MALDI-TOF/MS was used to analyze its structure. The predicted structure of lipid A and its mass-to-charge ratio peaks are shown at the top. (C) The WT, ΔpmrA, ΔpmrB, and CM012S (PmrB P233S-activated mutant strain) strains were prepared at an OD600 of 0.001 and were incubated with the various indicated concentrations of AlCl3 for 24 h. Absorbance A600 was monitored, and growth ability was expressed as a relative value, with the value without AlCl3 addition set at 100%. (D) PmrB motif mutant strains (ExxE/ExxxE alanine substitution strain) and various LOS modification gene disruption strains (ΔpmrCΔeptA, ΔnaxD, ΔpmrCΔeptAΔnaxD) were grown in LB broth containing 2 mM AlCl3 for 24 h. A600 of the bacteria was measured, and the relative growth inhibition was calculated by subtracting the value from 100%. All experiments were performed in triplicate. Mean values and error bars represent standard deviations. Statistical significance is shown as a reference of the WT strain value using Dunnett’s test; ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05.