Figure 2. CMTM6 promotes stability of cell surface CD58 and interacts with CD58.
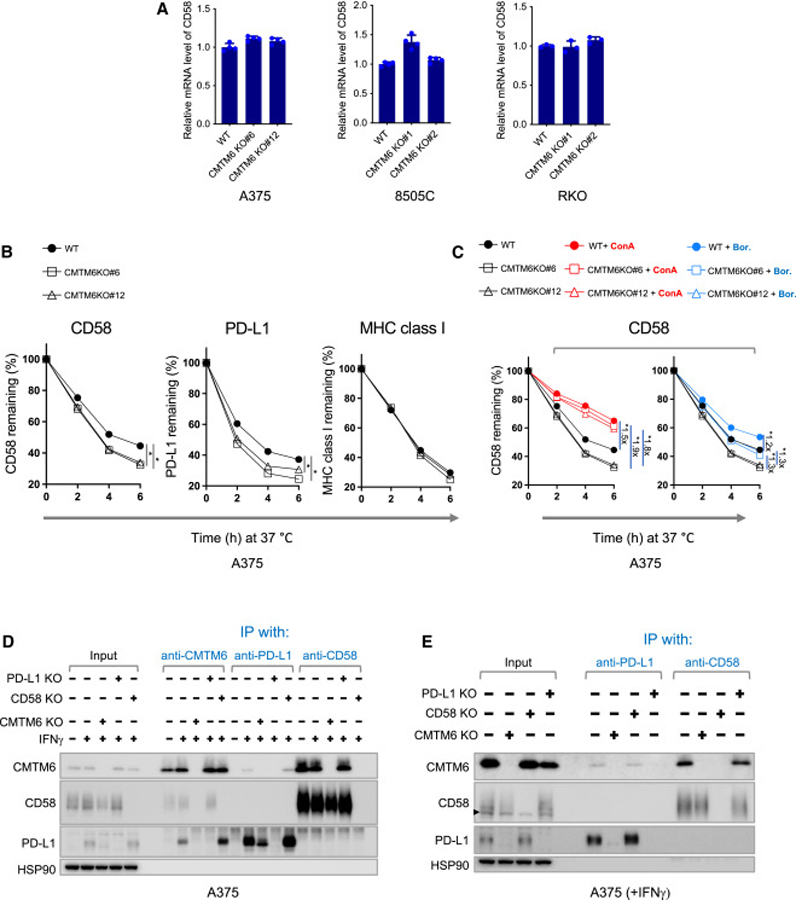
(A) qPCR analysis of mRNA levels of CD58 in CMTM6-deficient and -proficient A375, 8505C, and RKO cells.
(B) Stability of cell surface-expressed CD58, PD-L1, and MHC class I in parental (WT) and CMTM6-deficient (CMTM6 KO#6, CMTM6 KO#12) A375 cells. A375 cells were treated with IFNγ for 24 h and then individually incubated with APC-conjugated antibodies specific for CD58, PD-L1, or MHC class I at 4°C. After removing unbound antibodies, the cells were further incubated at 37°C for the indicated time periods, and the APC signal was measured by flow cytometry. The percentage of signal remaining at the indicated time points relative to time 0 is shown.
(C) Stability of cell surface-expressed CD58 in the parental (WT) and CMTM6-deficient (CMTM6 KO#6, CMTM6 KO#12) A375 cells in the presence of the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib (Bor.) or the lysosome inhibitor concanamycin A (ConA). The untreated samples presented in (B) served as the control. Data acquisition and presentation were performed as described in (B).
(D) Western blot analysis of cell lysates and indicated immunoprecipitates from A375 cells. HSP90 served as a control.
(E) Western blot analysis of cell lysates and indicated immunoprecipitates by cell surface immunoprecipitation from A375 cells. For the cell surface immunoprecipitation, live cells were incubated with antibodies that recognize the extracellular domains of CD58 or PD-L1. After removal of unbound antibodies, the cells were lysed for (co)immunoprecipitation. HSP90 served as a control. The triangles indicate the position of background bands, which are present when the anti-CD58 antibody (R&D Cat# AF1689) was used for detection, whereas the anti-CD58 antibody (BioLegend, Cat# 330924) does not produce such background signal. Data represent mean ± standard deviation of at least triplicates (A–C) and were analyzed using unpaired Student’s t test. Statistical significance is indicated by *p < 0.05.
