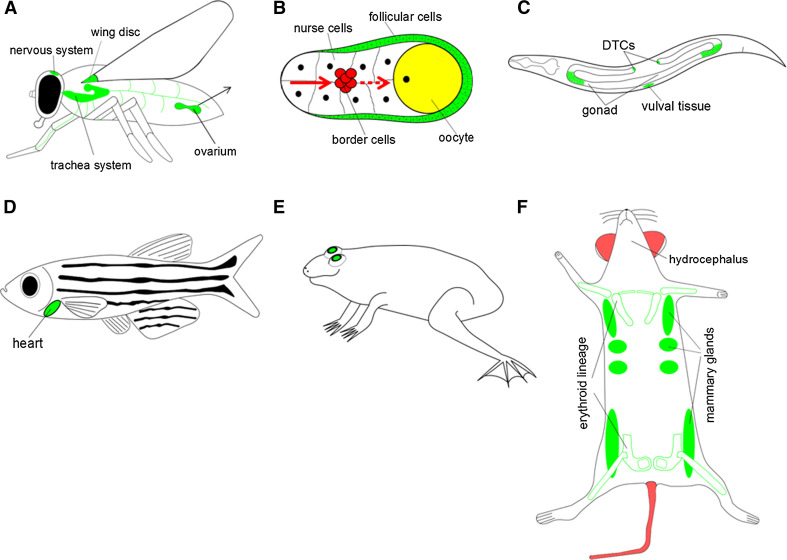
Fig. 1.
NDPK-related developmental functions in different model systems. Note that many signaling events, where the functions of NDPKs were observed actually operate during embryogenesis or later developmental stages, but the locations of relevant cells (or their descendants), tissues or organs are shown here schematically in the appropriate adult organism. Green labeling indicates the site of NDPK’s function. a The Drosophila NDPK homolog AWD is involved in the development of imaginal discs, also in the wing disc. The absence of awd function leads to defects in neurotransmission, ectopic migration of tracheal cells and female sterility. Thus, AWD’s function is linked to the nervous system, the developing trachea and the ovarium (detailed in b). b The fly egg chamber is composed of the germ cell complex (nurse cells and the oocyte), which is surrounded by follicular (epithelial) cells. Throughout Drosophila oogenesis, awd is expressed in follicular epithelial cells to ensure epithelial integrity. A group of follicular cells delaminating from the epithelium called border cells (marked by red) migrate towards the oocyte to form the micropyle. In the border cells awd expression is downregulated. c In C. elegans, NDK-1 functions during vulval and gonadal development, as well as participates in the migration of distal tip cells (DTCs) and engulfment of apoptotic germ cell corpses. d Knockdown of NME2 in zebrafish embryos leads to decreased cardiac contractility and impaired vessel formation. e Frog NM23-X4 is needed for retinal development. f Nme1 −/− mutant female mice display nursing disability because of growth retardation of the mammary glands and defects in the final step of mammary duct maturation of the nipple. Nme2 −/− deficient mice have no obvious defects, but show an altered immune response, reduced Ca2+ reuptake in the kidney and impaired pathological angiogenesis. Nme1 −/−/Nme2 −/− double knockout mice die perinatally due to failure of erythroid lineage development. Nme7 knockout mice present defects, like hydrocephalus, which can be linked to impaired motility of cilia causing abnormal ependymal flow