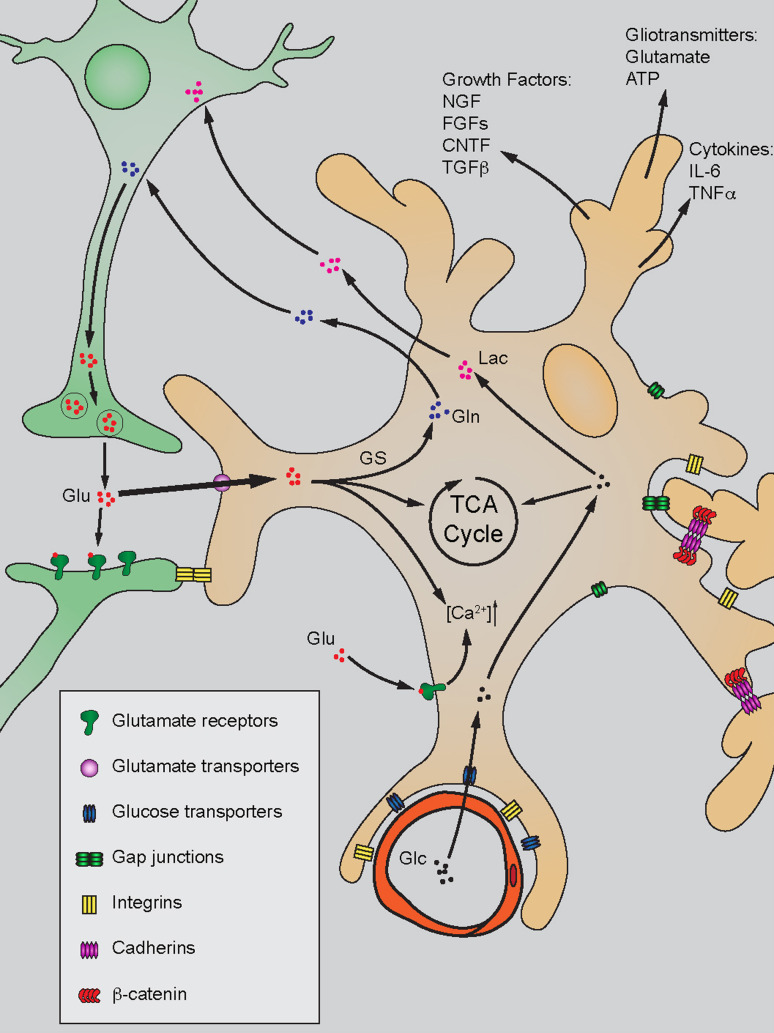
Fig. 1.
Primary functions of astrocytes in the quiescent stage. Astrocytes establish contact inhibition with other brain cells by gap junction, integrin, and cadherin-mediated mechanisms. They modulate CNS homeostasis by releasing growth factors, gliotransmitters, and cytokines. Astrocytes efficiently uptake glutamate (Glu) released from pre-synaptic neurons through glutamate transporters on plasma membrane. Internalized Glu is mainly involved in glutamine (Gln) production catalyzed by glutamine synthetase (GS), and released for neuronal use. Glu can also be utilized in the TCA cycle as well as induction of intracellular calcium signaling ([Ca2+]). Additionally, astrocytes take up glucose (Glc) from the blood and transport its metabolite lactate (Lac) to the neuron