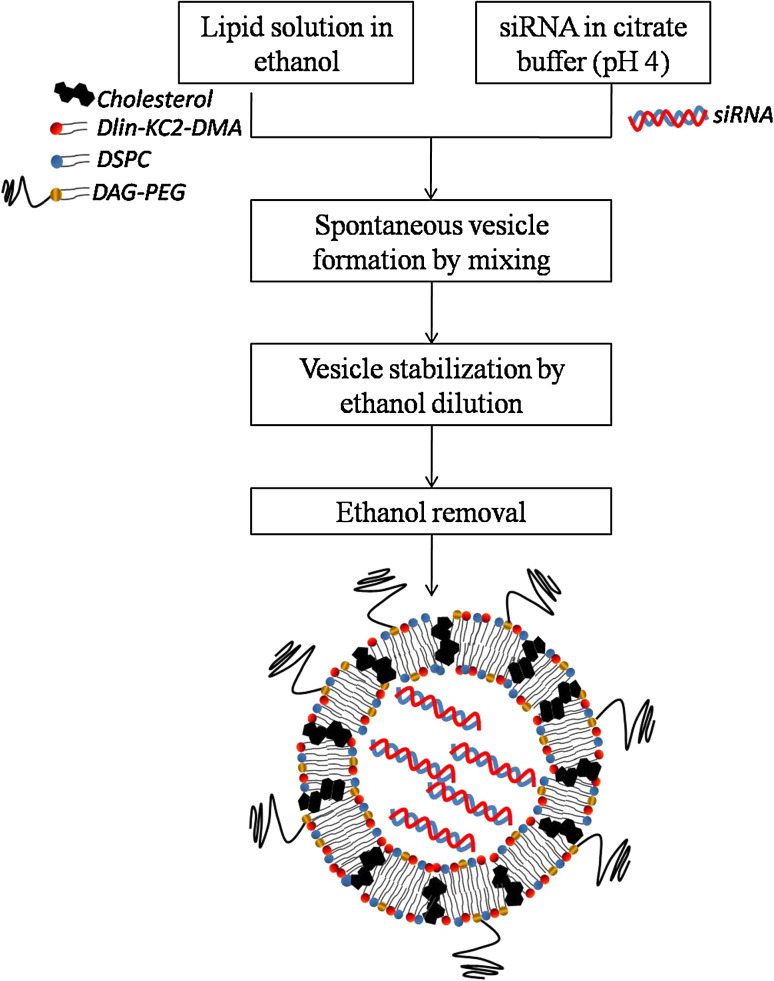
Fig. 4.
Ethanol dilution method of siRNA encapsulation. Liposomes are spontaneously formed upon mixing the lipids dissolved in ethanol with the siRNA dissolved in an aqueous buffer at acidic pH. The dilution of ethanol below the lipid solubility favors vesicle stabilization, which has the major advantage of avoiding an additional extrusion step to obtain small and homogenous liposomes [54]. The final liposomes have a surface charge close to neutrality, a mean size around 80 nm (or even smaller), and siRNA encapsulation efficiencies higher than 90 % [33, 55]