Fig. 3.
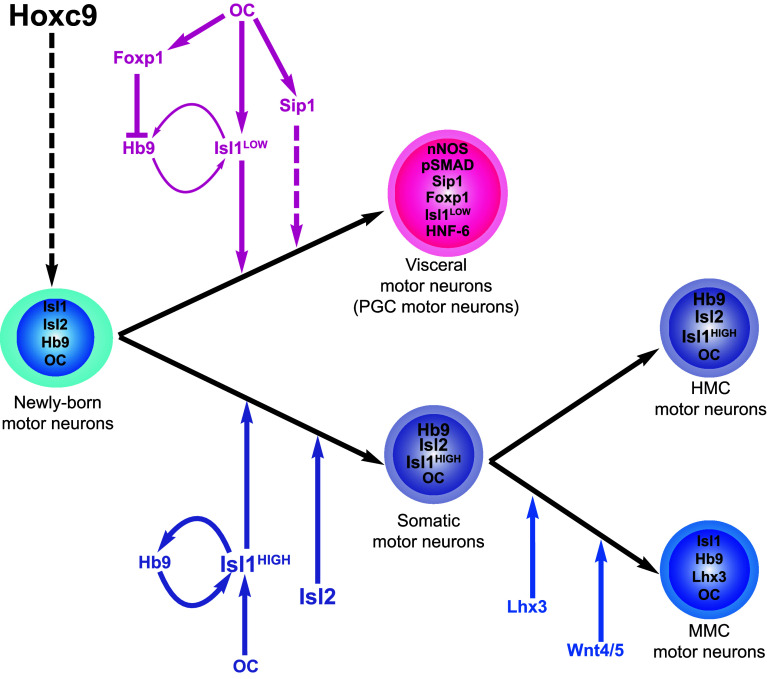
MN diversification at thoracic levels of the spinal cord. Hoxc9 establishes thoracic MN identity. The differentiation into somatic or visceral MN is finely tuned by the combined action of OC, Foxp1, Hb9, and Isl proteins. In some newly born MNs, OC factors and a mutual stimulatory loop between Hb9 and Isl1 triggers high Isl protein levels and somatic MN differentiation. In other newly born MNs, OC stimulate Foxp1 expression, which represses Hb9 and thereby weakens the mutual stimulatory loop between Hb9 and Isl1 and reduces Isl levels, which favors visceral MN differentiation. OC also promote Sip1 expression, which supports the generation of PGC cells. Among somatic MNs, Lhx3 and activation of Wnt signaling pathway promote the differentiation of MMC neurons. The HMC fate may constitute the default differentiation fate. nNOS neuronal nitric oxide synthase