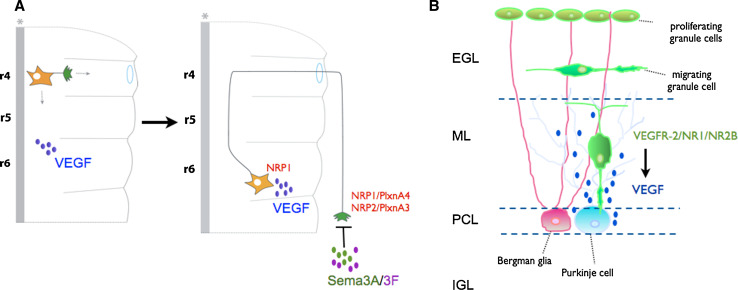
Fig. 1.
VEGF regulates neuronal migration. a VEGF controls migration of FBM neurons in the hindbrain. VEGF164 binds to NRP1 expressed in the FBM soma and controls their migration in the soma from rhombomere 4 (r4) to rhombomere 6 (r6). Axon guidance of these neurons is not controlled by VEGF164 but instead by semaphorin3A and semaphorin3F (SemaA/3F) which signal to receptor complexes formed by NRP1/PlxnA4 or NRP2/PlxnA3, respectively (adapted from Schwarz et al. [27]). b VEGF controls cerebellar granule cell migration during development. VEGF is expressed in Purkinje cells and controls granule cell migration from the external granule cell layer (EGL) towards the internal granule cell layer (IGL). Granule cells express VEGFR-2. VEGFR-2 forms a complex with NMDARs (NR1/NR2B) and VEGF signaling via VEGFR-2 induces the formation of VEGFR-2/NR1/NR2B receptor complexes and potentiates NMDAR-mediated currents and Ca2+ influx to control granule cell migration