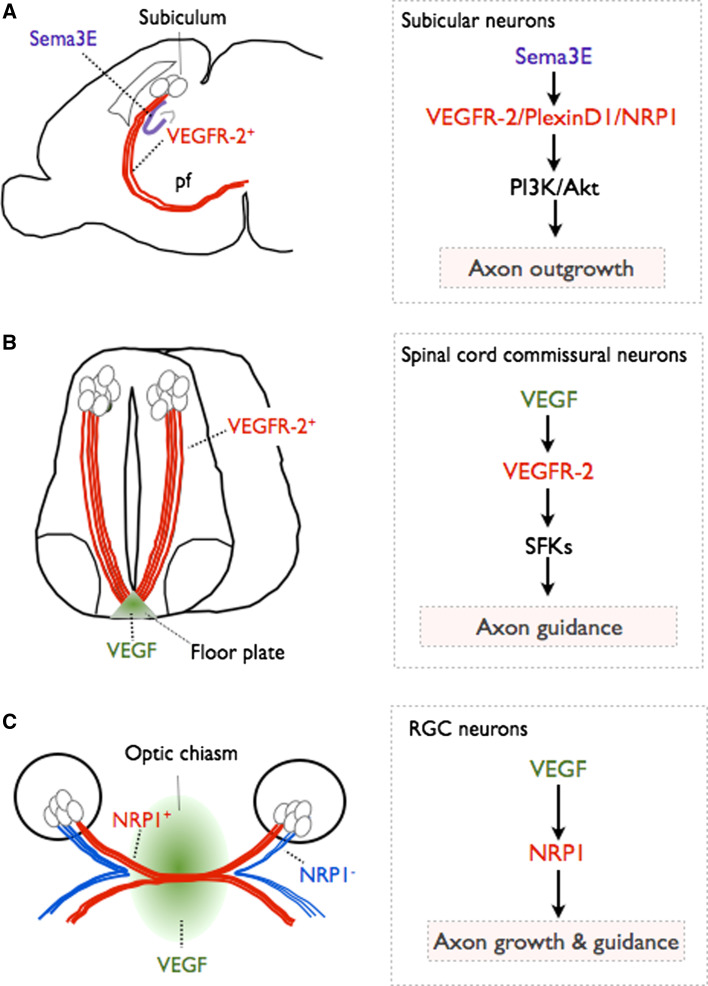
Fig. 2.
VEGF regulates axon growth and guidance. a VEGFR-2 regulates axon outgrowth of subicular neurons. Subicular neurons extend their axons (red) from the subiculum through the postcommissural fornix tract (pf). Sema3E is expressed in the CA1 and CA3 fields of the hippocampus (blue). Subicular neurons express VEGR-2. In these neurons, VEGFR-2 forms a multiprotein complex with NRP1 and PlexinD1 and becomes activated in a Sema3E-dependent/VEGF-independent manner. Activation of VEGFR-2 leads to activation of PI3K/Akt and axon growth. b VEGF regulates commissural axon guidance at the spinal cord midline. During spinal cord development VEGF is expressed in the floor plate (green). Commissural neurons and their axons projecting towards the ventral midline express VEGFR-2 (red). Floor plate-derived VEGF signals to VEGFR-2 in commissural axons, activates SFKs at the growth cone and induces growth cone turning, thus controlling axon guidance. c VEGF controls retinal ganglion cell (RGC) axon growth and guidance at the optic chiasm. VEGF is expressed at the optic chiasm (green). Certain RGC axons express NRP1 (red). VEGF binds to NRP1 and guides the axons across the midline to project in the contralateral side. NRP1− RGC axons do not sense VEGF and are not attracted to the midline, and instead project ipsilaterally (blue)