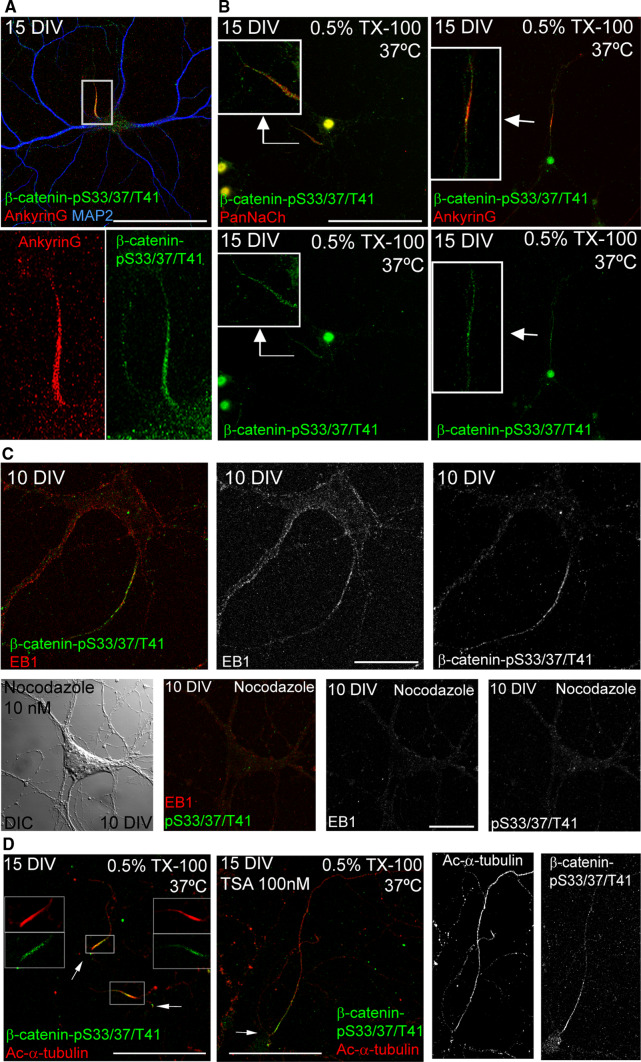
Fig. 4.
β-catenin-pS33/37/T41 is resistant to detergent extraction at the AIS and its location depends on microtubules. a 15-DIV hippocampal neurons stained with antibodies against AnkyrinG (red) and β-catenin-pS33/37/T41 (green). Box indicates the amplified region of the AIS shown in lower panels. b 15-DIV hippocampal neurons treated with cytoskeletal buffer (see “Materials and methods” section) for 10 min at 37 °C. After fixation, neurons were stained with β-catenin-pS33/37/T41 and Pan-sodium channel antibodies (left panels) or β-catenin-pS33/37/T41 and ankyrinG antibodies (right panels). Insets show enlarged views of axon initial segments. c 10-DIV hippocampal neurons cultured in the absence or presence of nocodazole (10 nM) from 7 to 10 DIV. Neurons were treated with cold methanol (−20 °C) for 5 min before fixation with PFA 4 % and stained with antibodies against EB1 (red) and β-catenin-pS33/37/T41 (green). A DIC image of nocodazole-treated neurons was obtained to identify the position of the soma. d Acetylated-α-tubulin and β-catenin-pS33/37/T41 staining of control or 100 nM TSA-treated 15-DIV neurons extracted with 0.5 % Triton X-100. Note that β-catenin-pS33/37/T41 and acetylated-α-tubulin co-localize at the AIS in control neurons, while β-catenin-pS33/37/T41 is no longer restricted to the AIS and is located along the axon following acetylated-α-tubulin pattern, as previously shown [10]. Arrows indicate soma position. Scale bar 100 µm in a, b and d, 20 µm in c