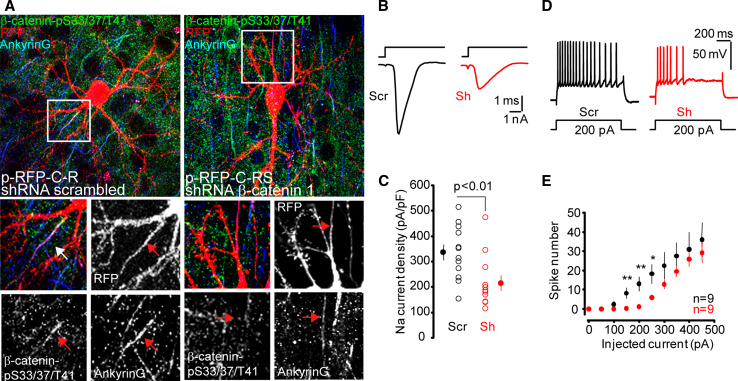
Fig. 8.
β-catenin interference diminishes ankyrinG and β-catenin-pS33/37/T41 expression at the AIS, voltage-gated sodium channel current and action potential firing in brain slices. a Representative cortical neurons in mice brain slices expressing RFP and scrambled or β-catenin shRNAs. Brain slices were obtained from P8 mice, cultured for 2 days prior to plasmids delivery to neurons by GeneGun. Plasmid expression was allowed for 7 days before electrophysiological recordings and fixation. Slices were stained with antibodies against β-catenin-pS33/37/T41 (green) and ankyrinG (blue). Insets show a magnification of the AIS region. Arrows indicate AIS position. Note that in neurons expressing β-catenin interference shRNA, β-catenin-pS33/37/T41 immunoreactivity is absent at the AIS and ankyrinG intensity is reduced compared to scrambled neurons. Scale bar 50 µm. b Sodium currents measured in L5 pyramidal neurons expressing the β-catenin shRNA 1 plasmid (Sh) or the scrambled shRNA (Scr) were evoked by a depolarizing step from −80 to −20 mV. c Plot of the sodium current density for test (Sh) and control (Scr) neurons. Note the significant reduction in the current density (unpaired t test). d Representative firing profiles for Scr and Sh neurons. e Input–output curves for Scr and Sh neurons. Note the significant reduction in excitability for Sh neurons (unpaired t test, ** p < 0.01, *p < 0.02)