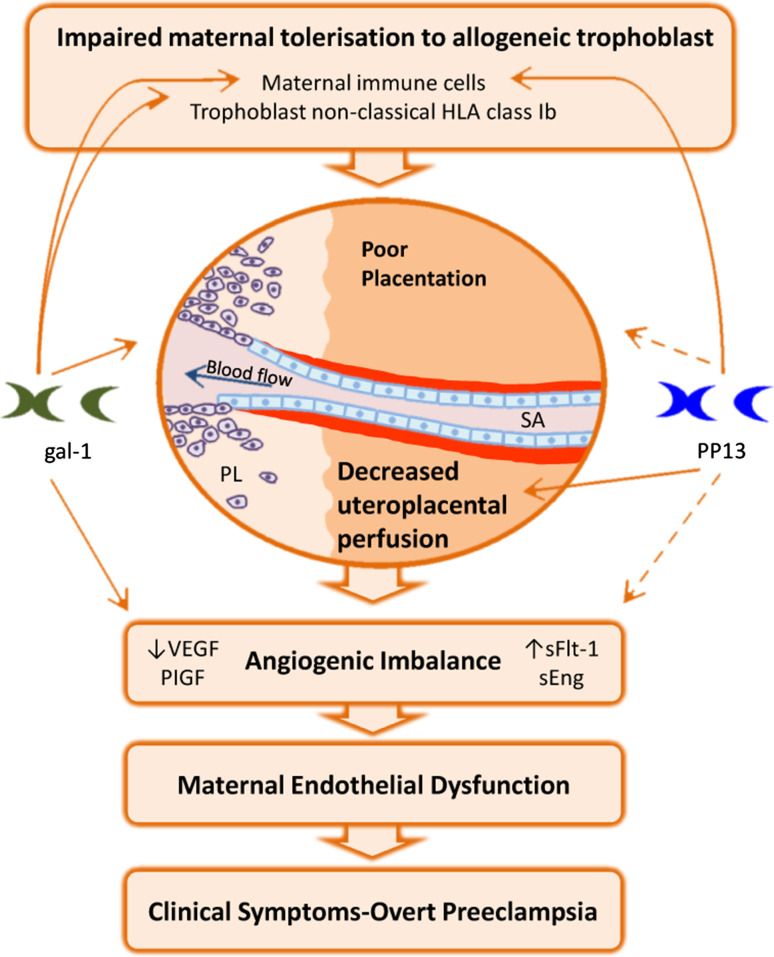
Fig. 2.
Regulatory functions of galectins involved in the pathogenesis of PE. Both gal-1 and PP13 may paly an important immunomodulatory function during early stages of pregnancy by regulating maternal T cell survival and activation. Additionally, gal-1 appears to be important for the control of trophoblast lineage differentiation along the invasive pathway, thereby directly influencing the process of placentation and immunomodulation by inducing HLA-G expression on EVTcells. The precise function of PP13 during placentation is still elusive, but this lectin showed the ability to increase blood flow to the implantation site by influencing uteroplacental arterial remodeling. Pro-angiogenic properties of galectins and their interactions with the VEGF signaling pathway may, when deregulated, contribute to the angiogenic imbalance typical of the syndrome. This has been clearly demonstrated for gal-1 in vitro and in vivo, but direct effects of PP13 in the regulation of angiogenesis await further investigation