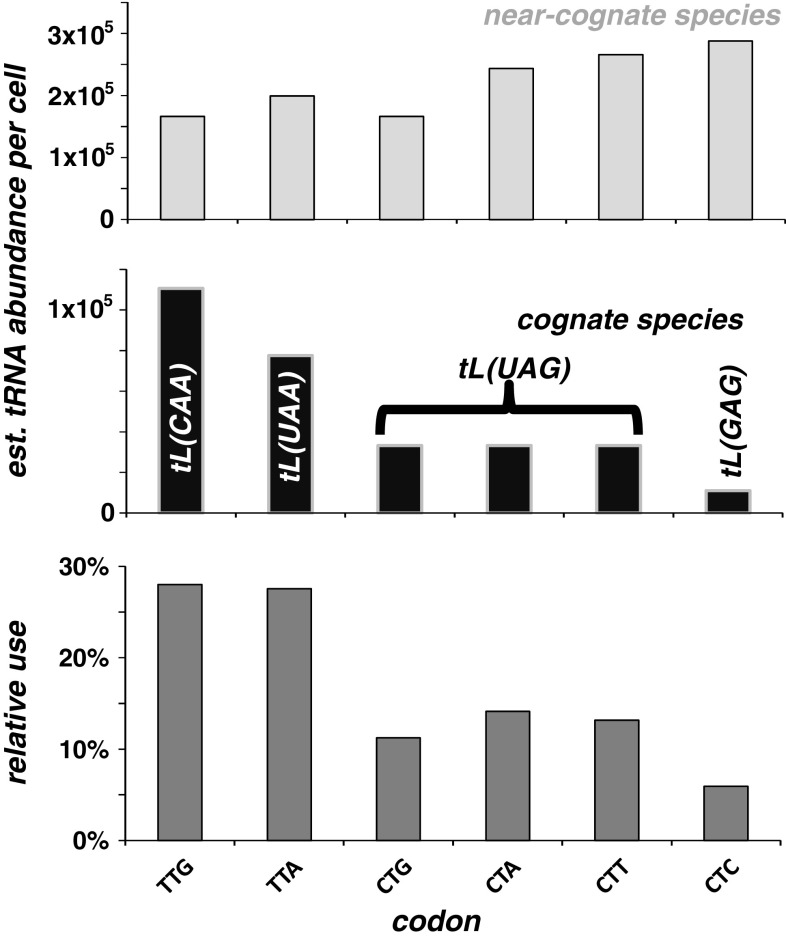
Fig. 3.
An illustration of the different baker’s yeast tRNA groups that act on the six possible leucine codons. TTG, TTA and CTC are decoded by separate cognate tRNA species, whereas CTG, CTA and CTT are decoded by one cognate wobble-decoding tRNA species. Near-cognate tRNAs do not normally lead to codon decoding but are slow to be rejected by the ribosome. Cognate tRNAs usually lead to codon decoding and peptidyl transfer when they enter the ribosomal A-site. Thus, the near-cognate:cognate ratio determines the average wait-time until the first cognate tRNA enters the ribosome and peptidyl transfer occurs, and the relative usage of the different codons usually correlates with this ratio