Fig. 6.
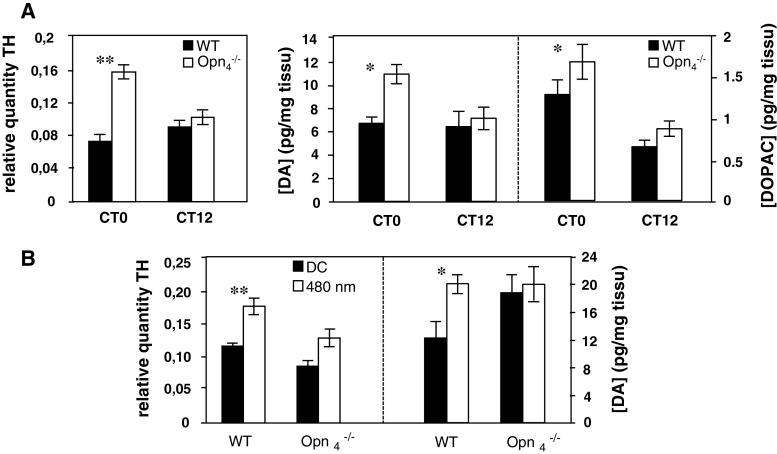
A Left panel Circadian expression of tyrosine-hydroxylase (TH) mRNA in wild-type and Opn −/−4 mouse (n = 5 for each genotype). Animals were sacrificed at two circadian times CT0 and CT12 and TH mRNA was quantified by real time RT-PCR. In the wild-type mouse, the level of TH mRNA was constant between CT0 and CT12 whereas in the Opn −/−4, a significantly increase (p ≤ 0.01) was observed at CT0 compared to the control mouse. Right panel Dopamine (DA) and DOPAC concentrations in wild-type and Opn −/−4 mouse (n = 9–11 for each genotype). Post hoc Newman–Keuls test shows significant differences in DA and DOPAC level between genotypes at CT0 (p < 0.05), whereas no significant differences were observed at CT12. B Light induction of TH mRNA (n = 5 for each genotype) and DA content (n = 7–10 for each genotype and for dark and light conditions) in wild-type and Opn −/−4 mouse. A single light pulse (480 nm, 15 min, 2.8 × 1014 photons/cm2/s) was administered at CT16. Animals were sacrificed 30 min after the beginning of the light pulse.TH mRNA induction by light was quantified by real time RT-PCR and DA content by HPLC. In the wild-type mouse, light significantly induces TH mRNA (p < 0.01) and DA concentration (p < 0.05) whereas in the Opn −/−4, no increase was observed compared to the dark control