Fig. 2.
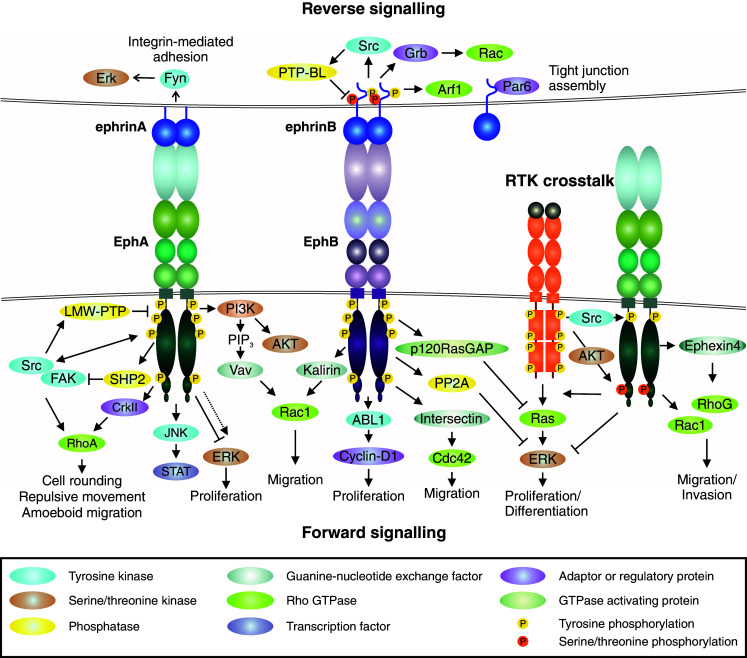
Eph/ephrin signaling. Eph forward signaling (bottom). Ligand binding at cell–cell contact (or involving soluble shed ligand) triggers receptor clustering and phosphorylation of tyrosine residues in juxtamembrane and tyrosine kinase domains [12, 26, 33–36]. The ligand-induced Eph activation mediates downstream signaling pathways such as PI3K–Akt, Janus kinase (JNK)-STAT, as well as focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and Src kinase-mediated signals [2, 3, 47–49]. Forward signaling can also induce transient ERK activation, although the overall effect of EphAs on ERK activity appears suppressive, as e.g., loss of EphA2 results in increased overall Ras/ERK pathway activation [12, 61, 65, 154, 214, 215]. Eph forward signaling also regulates Rho GTPase-mediated actin dynamics through interaction with guanine exchange factors (GEFs), e.g., Ephexin and Vav (EphA), as well as Kalirin and Intersectin (EphB) [17, 82–86]. Low molecular weight protein tyrosine phosphatase (LMW-PTP) activated by Src regulates Eph signaling attenuation or termination by receptor dephosphorylation [82]. Ephrin reverse signaling (top). Eph-ephrin interaction triggers intracellular signaling into the ligand-expressing cell. Reverse signals through GPI-anchored ephrinAs rely on lipid raft-mediated clustering with proteins such as Src family kinase (Fyn) to induce e.g., ERK signaling [53, 87]. EphB/ephrinB interaction triggers reverse signals more directly via ephrinB cytoplasmic tail phosphorylation followed by recruitment of SH2-domain-containing proteins such as Src and Grb4, as well as Rac1 activation, which is attenuated by EphB dephosphorylation by PTP-Basophil-like (PTP-BL) phosphatase [90, 93]. EphrinBs also recruit PDZ-domain-containing proteins through their C-terminus [90], whereas non-phosphorylated ephrinB1 can interact with PAR6, promoting tight junctions [97]. Receptor tyrosine kinase crosstalk (middle right). EphA overexpression coupled with low expression of ephrinA ligand is associated with low tyrosine phosphorylation of the ligand-unbound receptor [32]. Akt downstream of growth factor receptors phosphorylates ligand-unbound EphA2 at serine residue (Ser897) [32, 101]. Src activation can regulate ligand-independent EphA signaling [22, 118]. RTK-EphA2 crosstalk promotes Rho-GTPase activities and EGF-induced Ras/ERK pathway activation in proliferating/differentiated cancer cells whereas suppression of the differentiation-promoting ERK activity in tumor-propagating cells (TPCs) in glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is mediated by serine-phosphorylated EphA2 [10, 83, 86, 101]
