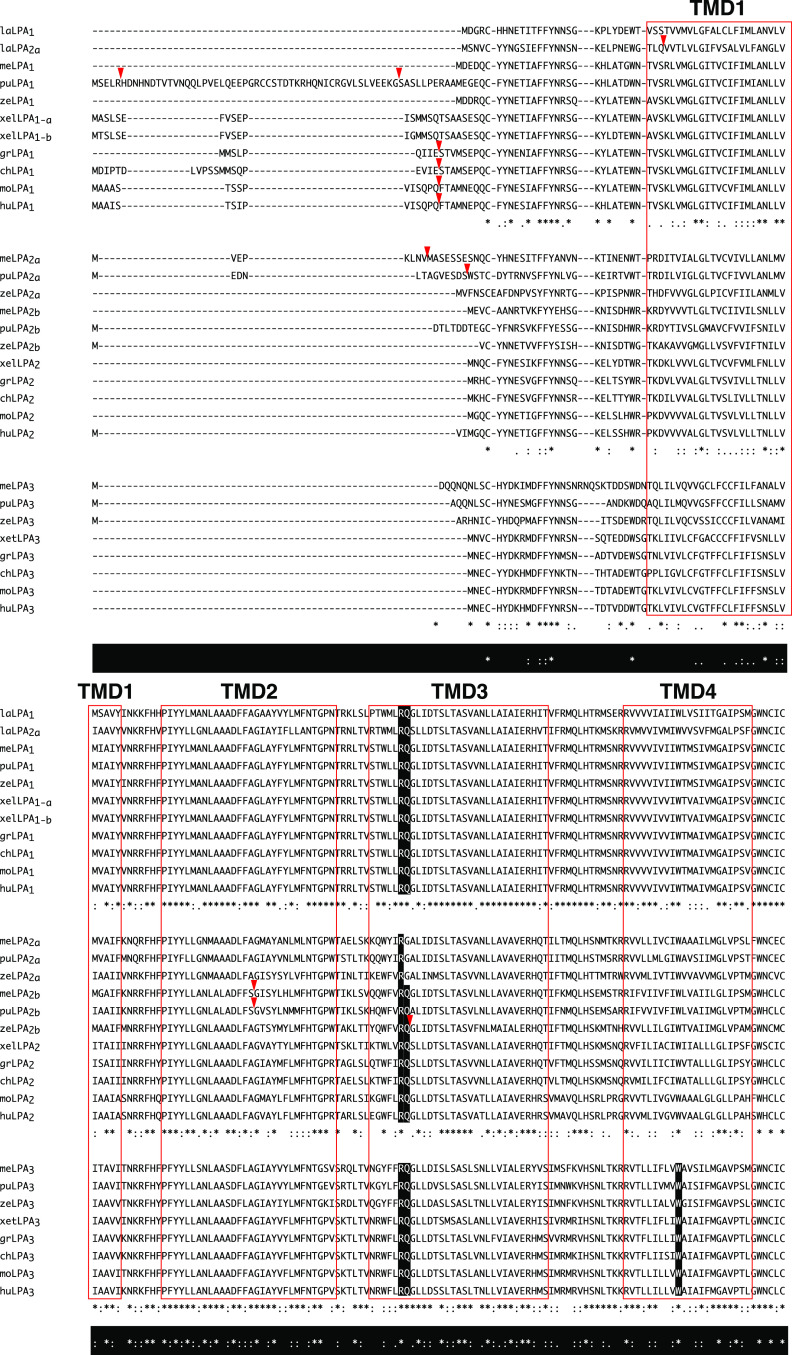
Fig. 1.
Multiple sequence alignment for edg family LPA1–LPA3. The multiple sequence alignment was performed using the MAFFT web service (http://mafft.cbrc.jp/alignment/server/). The GenBank accession numbers for the LPA receptors used in this analysis are shown in Table 1. Red boxes indicate the seven putative transmembrane domains (TMD1–TMD7). Red arrowheads indicate the exon–intron boundary in the coding regions of the genes. Asterisks (*), colons (:), and periods (.) below each human LPA receptor sequence indicate no substitutions (identical), conserved substitutions, and semi-conserved substitutions across all animal species for each LPA receptor subtype, respectively. Asterisks (*), colons (:), and periods (.) in white on a black background below the LPA receptor sequences indicate no substitutions, conserved substitutions, and semi-conserved substitutions, respectively, across all animal species for LPA1–LPA3. Residues involved in LPA binding are shown in white on a black background. me medaka, pu pufferfish, ze zebrafish, xel Xenopus lavies, xet X. tropicalis, gr green sea turtle, ch chick, mo mouse, hu human