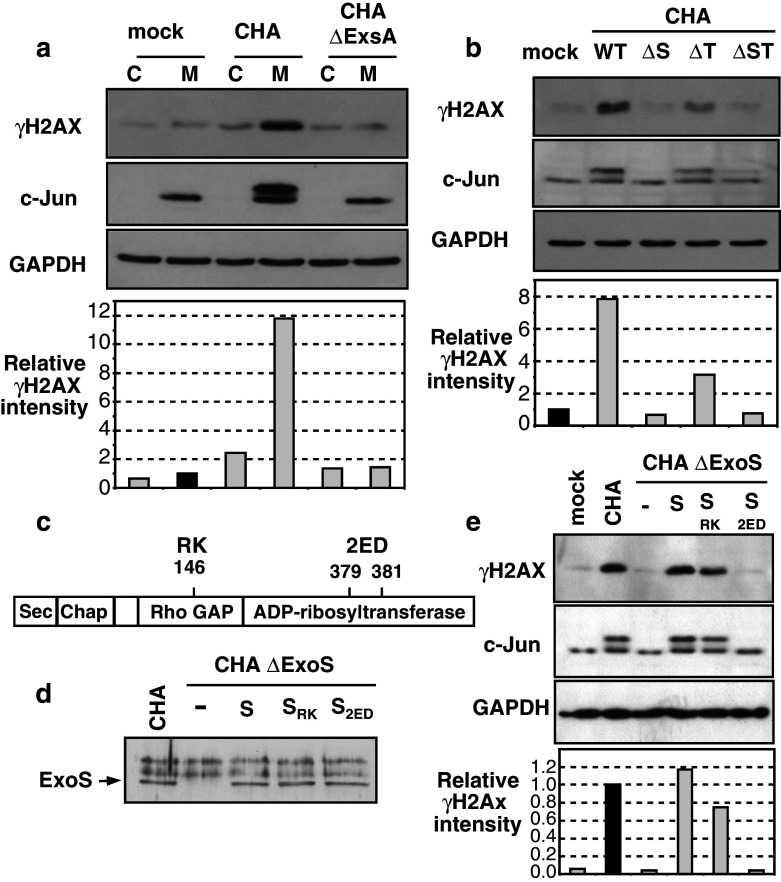
Fig. 5.
Essential roles of T3SS and ExoS ADP-ribosyltransferase activity in γH2AX induction. a Undifferentiated HL60 cells (C) or HL60 macrophages (M) were infected with wild-type P. aeruginosa CHA strain (CHA) or a mutant strain with a deleted exsA gene and devoid of T3SS activity (CHAΔExsA), both at a MOI of 10. Cells extracts were analyzed by Western blot with the indicated antibodies. γH2AX relative intensity normalized to GAPDH level was set to 1 in mock macrophages (dark bar) for panel a and b. b HL60 macrophages were infected with a wild-type CHA strain (WT), or with isogenic strains with deletions of exoS (ΔS), exoT (ΔT) or both exoS and exoT (ΔST) genes. Western-blot analysis of cell extracts prepared 2.5 h post-infection. c Representation of the ExoS domains. Sec: secretion signal, Chap: zone of interaction with chaperone protein, RhoGAP and ADP-RT domains. RK indicates an inactivating mutation by replacement of an arginine with a lysine at position 146, 2ED indicates an inactivating mutation of the ADP-RT function by replacement of two glutamic acids with aspartic acids at positions 379 and 381. d Analysis by Western blot of ExoS secretion by CHA, CHAΔExoS, or CHAΔExoS complemented with wild-type ExoS (S), mutant ExoSRK (SRK), or mutant ExoS2ED (S2ED). The doublet above ExoS is non-specific. e HL60 macrophages were infected with CHA or the CHAΔExoS complemented strains described in (d), all at a MOI of 10. Cell extracts were prepared 2.5 h post-infection and analyzed by Western blot with the indicated antibodies. γH2AX relative intensity was set to 1 for macrophages infected with CHA (dark bar)