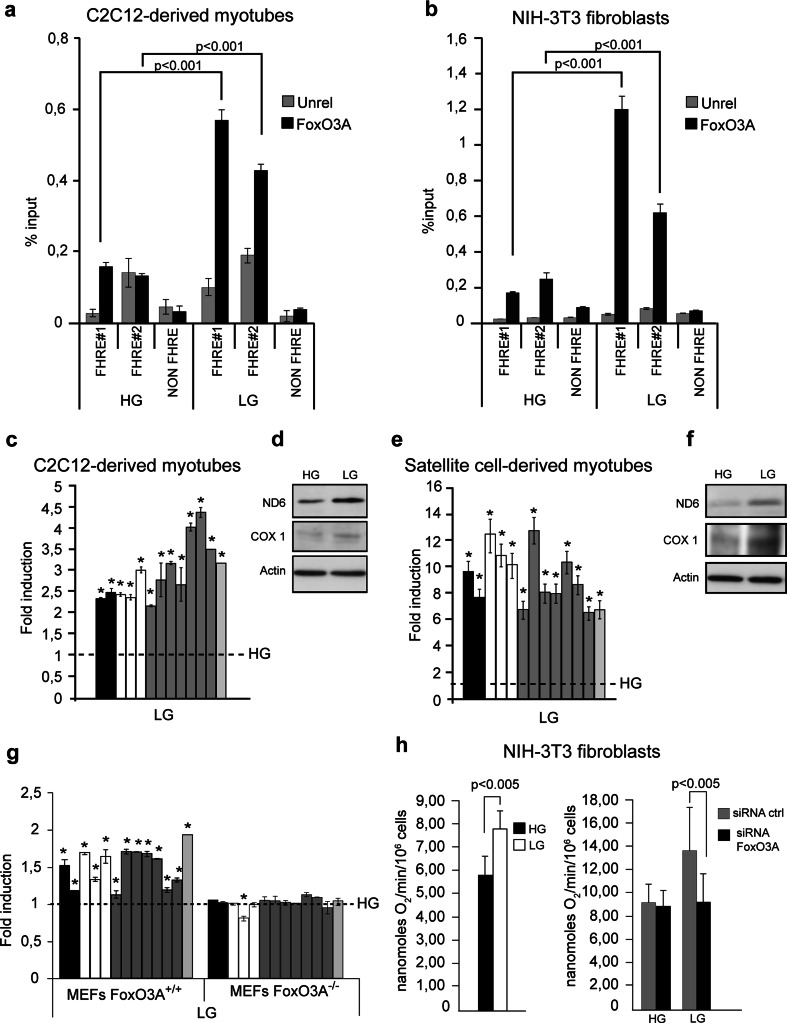
Fig. 2.
GR-dependent FoxO3A mitochondrial import leads to increased mitochondrial respiration. a, b Under GR conditions (LG 12 h), FoxO3A binds to two different target sites (FHRE#1: 14,963–15,110 bp; FHRE#2: 15,400–15,469 bp) on mitochondrial DNA in C2C12 myotubes (n = 5) (a) and NIH-3T3 fibroblasts (n = 5) (b). Signal specificity is confirmed by the analysis of a distal region not containing FHRE sites (NON FHRE, 8,653–8,768 bp). Unrel unrelated antibody (anti-IgG). Data are presented as mean ± SEM and significance was calculated with Student’s t test. c–g GR (LG) induces the upregulation of mitochondrial genes both at the RNA (c, e, n = 5) and the protein level (d, f, n = 3) in C2C12-derived (c LG 12 h, d LG 24 h) and primary satellite cell-derived myotubes (e LG 36 h, f LG 48 h). Upregulation of mitochondrial genes upon GR (LG 24 h) is blunted by the absence of FoxO3A in primary MEFs (n = 5) (g). h Upon genetic ablation of FoxO3A using a specific siRNA, GR (LG 36 h) fails to induce an increase in DNP-uncoupled mitochondrial endogenous respiration in murine NIH-3T3 fibroblasts (left panel n = 9, right panel n = 6). Data are presented as mean ± SEM and significance was calculated with Student’s t test. (c, e, g) black bars ATPase 6 and 8 genes, white bars COI, COII and COIII genes, grey bars ND1, ND2, ND3, ND4, ND4L, ND5, and ND6 genes, light grey bar cytochrome b gene. The dotted line corresponds to the expression levels detected in cells cultured in standard glucose conditions (HG). Data are presented as mean ± SEM, *p < 0.05