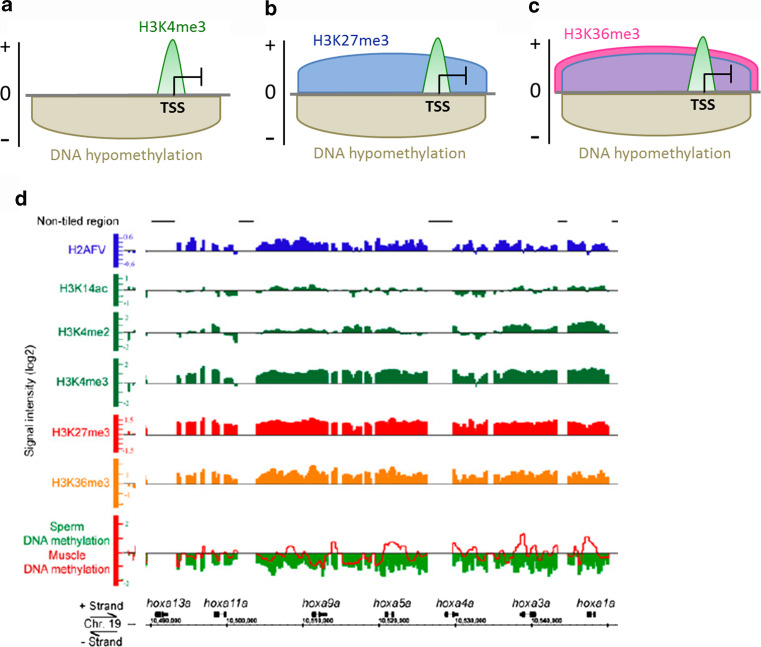
Fig. 1.
Marking of sperm chromatin by DNA methylation, post-translational histone modifications and histone variants. a–c DNA methylation and histone modification patterns detected on housekeeping and developmental gene promoters in zebrafish sperm. a H3K4me3 enrichment at the TSS of DNA hypomethylated genes involved in cellular homeostasis. b, c Promoters of developmentally regulated genes are also DNA hypomethylated and marked by H3K4me3 together with b H3K27me3, or c H3K27me3 and H3K36me3. d Multivalent marking of the hoxa locus by modified histones, histone variant and DNA (hypo)methylation in zebrafish sperm. These chromatin immunoprecipitation and array hybridization profiles depict occupancy in histone variant H2AFV (top track), and in the following histone modifications: H3K14ac (absent from the hoxa locus), H3K4me2, H3K4me3 (these three marks are transcriptionally permissive), H3K27me3 (transcriptionally repressive) and H3K36me3 (commonly associated with transcriptionally active genes in somatic cells). Note the overlapping domains marked by H3K4me3, H3K27me3, and H3K36me3. This domain is depleted of DNA methylation (bottom track, beige). Panel d is reproduced and modified from Ref. [18] with permission