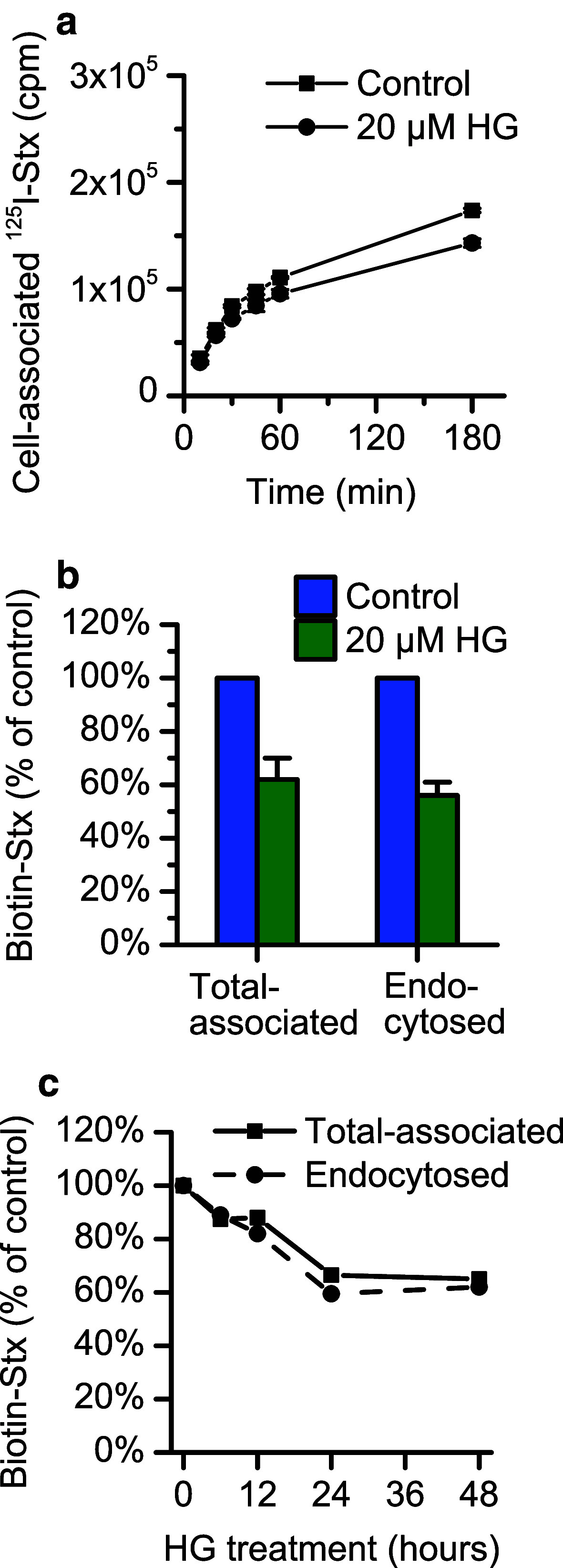
Fig. 3.
The binding of Shiga toxin is reduced after pretreatment with HG. a Shiga toxin binding in HEp-2 cells was determined by quantification of total cell-associated 125I-labeled Stx1-mut after 24-h pretreatment with 20 µM HG or 0.1 % (v/v) ethanol. The cells were incubated with 10 ng/ml toxin for the indicated times before removing the medium and measuring toxin associated with cells. The figure shows a representative experiment with each point representing mean ± deviation between two replicates. b Quantification of binding and endocytosis of Shiga toxin in HEp-2 cells after 24-h pretreatment with 20 µM HG or 0.1 % (v/v) ethanol (control) was performed using biotinylated Shiga toxin. After 20-min incubation with 40 ng/ml toxin, cells were lysed, and the lysates were incubated with streptavidin-coated beads and Ru(II)-labeled anti-Shiga toxin antibody. The total cell-associated Shiga toxin was determined by measuring the electrochemiluminescence produced by the Ru(II)-tag. To determine the amount of endocytosed toxin, half of the cells were treated with MESNa prior to lysis to remove biotin from non-internalized toxin at the cell surface. The figure shows the mean of three individual experiments ± standard error of the mean. c HEp-2 cells were incubated up to 48 h with 20 µM HG or 0.1 % (v/v) ethanol (control), and the total cell association and endocytosis of biotin-Shiga toxin were measured as previously described at each time point. The figure shows data from one representative experiment