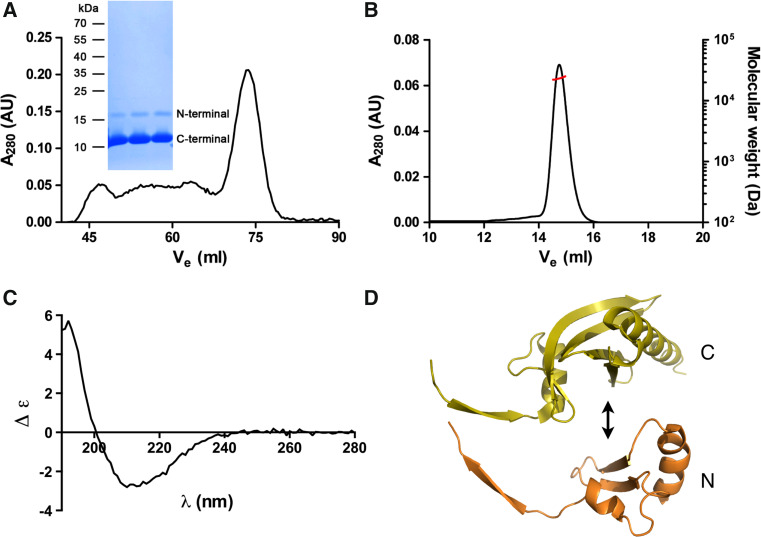
Fig. 6.
Purification of half-profilins. a The co-expressed profilin fragments co-elute from SEC in a single symmetric peak, which corresponds to the full-length wild-type Plasmodium profilin. Both N- and C-terminal profilin fragments were identified by mass spectrometry from a Coomassie-stained SDS polyacrylamide gel (inset) of the SEC peak fraction. b Static light scattering gives a molecular weight of 23 kDa for the complex of the profilin fragments. The left Y axis and the black line show the UV absorbance at 280 nm and the right Y axis the molecular weight (in Da) from the light scattering signal (red line). c CD spectrum of the complex of the two profilin fragments. d Putative assembly of the two profilin fragments. It seems likely that the long β extensions of each half (on the left) adopt a more disordered conformation