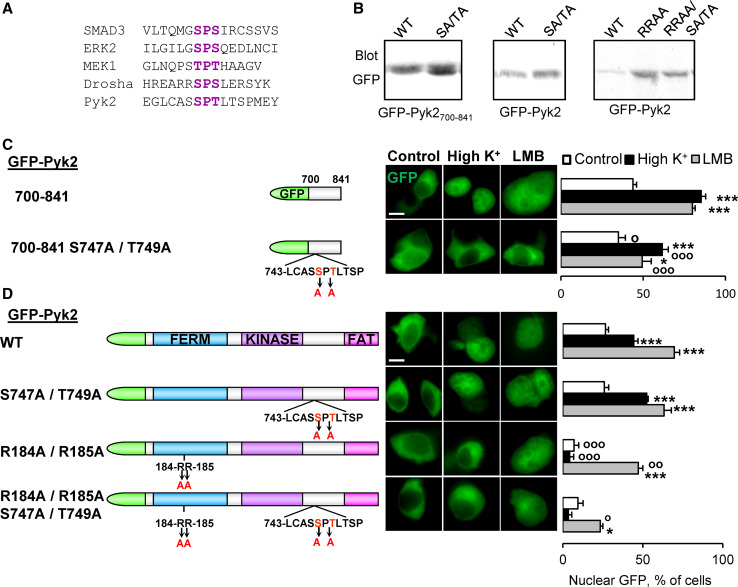
Fig. 2.
Pyk2700–841 contains an atypical nuclear import motif. a Sequence alignment showing the NTS identified in SMAD3, ERK2, MEK1, Drosha, and the putative Pyk2 NTS. b Anti-GFP immunoblotting of PC12 cells transfected with GFP-Pyk2700–841 or GFP-Pyk2, with the indicated mutations (S747A, T749A, R184A, and R185A). PC12 cells transfected with GFP-Pyk2700–841 (c) or GFP-Pyk2 (d) with the indicated mutations (scheme on the left) were treated with high K+ (High K+, 40 mM, 3 min), LMB (LMB, 11 ng/ml, 3 h), or control solution. GFP fluorescence and nuclei stained with DAPI (middle) were analyzed and the number of cells with n ≥ c GFP quantified (right). Values are means + SEM. c Two-way ANOVA: mutation effect F (1,23) = 26.92, p < 0.0001, treatment effect F (1,23) = 118.57, p < 0.0001, interaction F (1,23) = 5.48, p < 0.05. Newman–Keuls test: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 versus control. °p < 0.05, °°p < 0.01, °°°p < 0.001 versus WT. d Two-way ANOVA: p < 0.0001, mutation effect F (3,44) = 63.13, p < 0.0001, treatment effect F (1,44) = 14.55, p < 0.0005, interaction F (3,44) = 11.29. Newman–Keuls test: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 versus control. °p < 0.05, °°p < 0.01, °°°p < 0.001 versus WT. Scale bar 5 μm