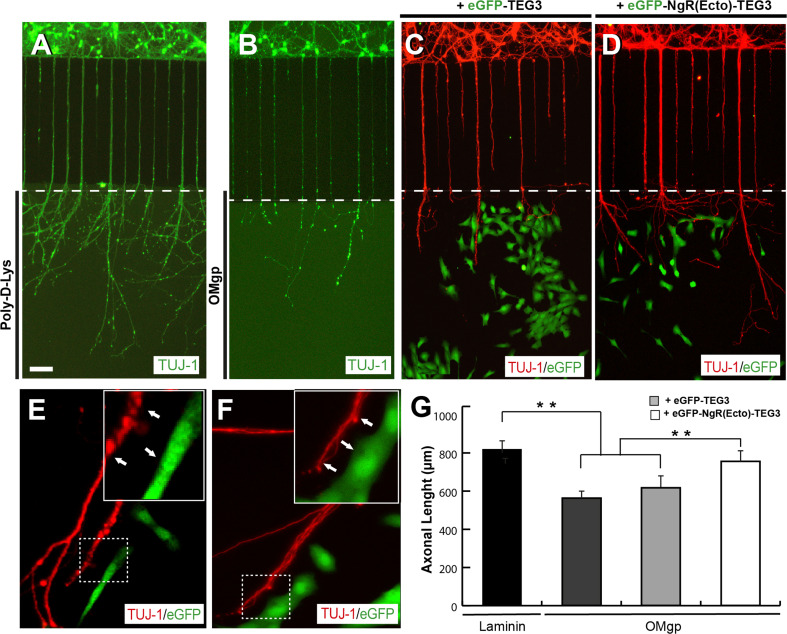
Fig. 6.
Increased axonal growth of cortical neurons induced by eGFP-NgR(Ecto)-TEG3 cells in microfluidic compartmentalized devices. a, b Photomicrographs illustrating examples of E15.5 cortical neurons cultured on Xona™ microfluidic devices coated with Poly-D-Lys (a) or OMgp (b) for 12 days (see Methods for details). c, d Examples of the combined co-culture of E15.5 cortical neurons and eGFP-TEG3 cells (c) or eGFP-NgR(Ecto)-TEG3 cells (d). After fixation, microfluidic devices were processed for TUJ-1 and eGFP immunostaining. e, f High power photomicrographs of double-labelled microfluidic devices containing cortical axons (red) and eGFP-NgR(Ecto)-TEG3 (green). Note that eGFP-NgR(Ecto)-TEG3 cells do not seem to be in contact with growing axons (arrows). g Histogram illustrating the quantitative results of the experiment illustrated in (a–d). The ends of the bridge channels are labelled by a white dashed line in (a–d). Data in (g) are represented as mean ± S.E.M. Scale bars a = 100 μm pertain to b–d. Asterisks in (g) indicate statistical differences (laminin vs OMgp t = 17.8; laminin vs OMgp + eGFP-TEG3 t = 16.43; OMgp + eGFP-TEG3 vs OMgp + eGFP- NgR(Ecto)-TEG3 t = 6.87; **P < 0.05; one-way ANOVA Bonferroni post hoc test)