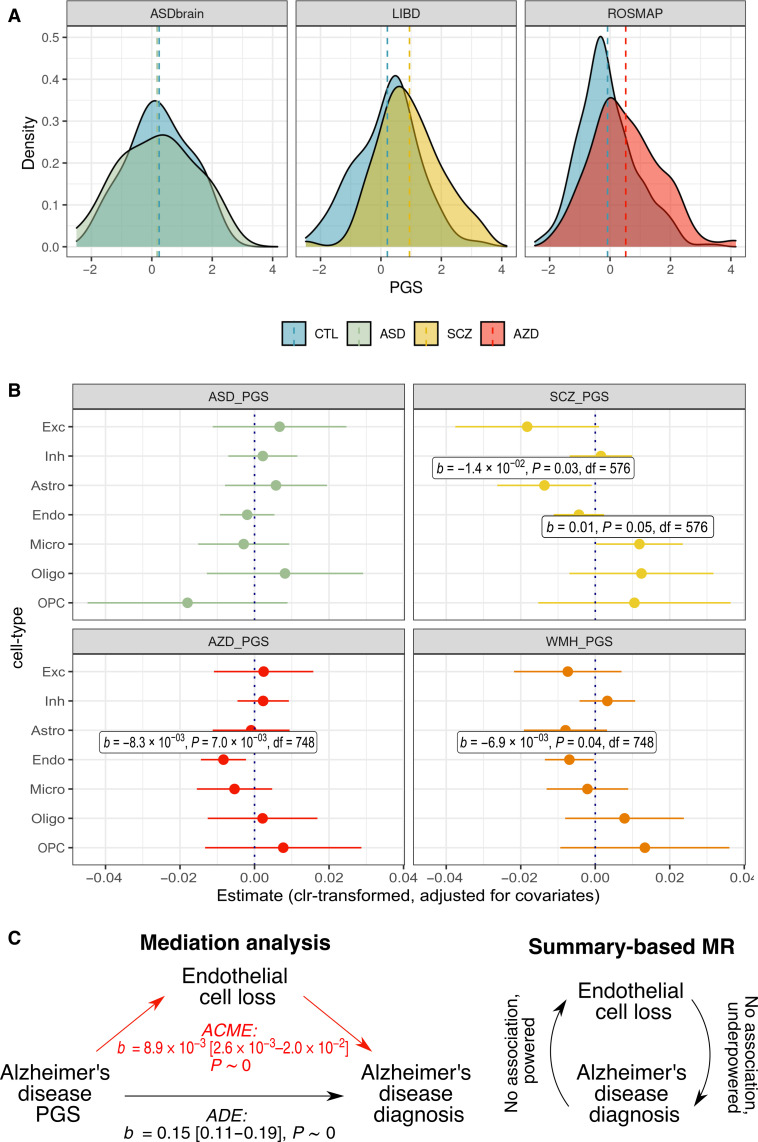
Fig. 4. Polygenic scores for neuropsychiatric traits predict brain cell-type shifts.
(A) Distributions of PGS within each study, comparing individuals with and without the neuropsychiatric diagnosis of interest. (B) Neuropsychiatric trait PGS coefficients (±95% CI) from linear models for brain CTP (clr-transformed) ~ neuropsychiatric trait PGS + age + age2 + diagnosis + sex + batch + genotyping PC1–3, subsetting for individuals with the diagnosis of interest (i.e., one of ASD, schizophrenia, or Alzheimer’s disease) and undiagnosed controls. Analyses included individuals with the diagnosis of interest and all controls: n = 531 for the ASD_PGS analysis, n = 591 for the SCZ_PGS analysis, and n = 763 for the AZD_PGS analysis. The White Matter Hyperintensity on MRI (WMH_PGS) PGS analysis included the same n = 763 individuals as for Alzheimer’s disease. (C) Schematic of causal analyses (mediation analysis and SMR). For the mediation analysis, statistics for effect sizes, 95% CI and P value are provided. ACME, average causal mediation effect; ADE, average direct effect.