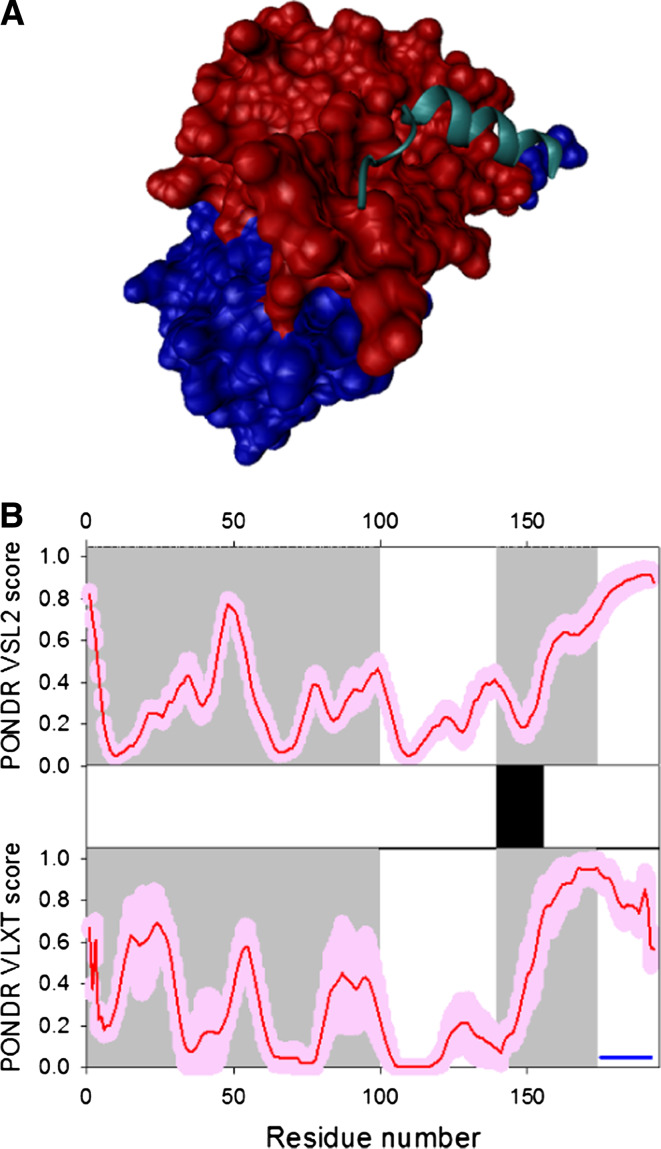
Fig. 17.
Disorder propensity and structural features of the HIV-1 viral infectivity factor (Vif protein). a Crystal structure of the Vif peptide 139–179 (which covers the HIV-1 Vif BC and Cullin boxes, cyan ribbon) in association with a complex of human ElonginB (red surface) and ElonginC (blue surface) (3DCG). b Intrinsic disorder prediction in Vif by PONDR® VSL2 (top panel) and PONDR® VLXT (bottom panel). Red line represents an averaged disorder score for Vif from ~50 different HIV-1 isolates. Pink shadow covers the distribution of disorder scores calculated for Vif from these isolates. Location of the α-helix seen in the crystal structure of the Vif-ElonginB-ElonginC complex is shown by the black bar between the disorder score panels. Gray shaded areas correspond to the NTD domain (residues 1–100) that contains an RNA-binding domain, and discontinuous binding sites for A3G and A3F, and to the SOCS box domain (residues 144–173) containing a BC-box region (residues 144–159) and a putative Cullin box (residues 159–173). Dark blue line shows the location of a predicted α-MoRF