Fig. 2.
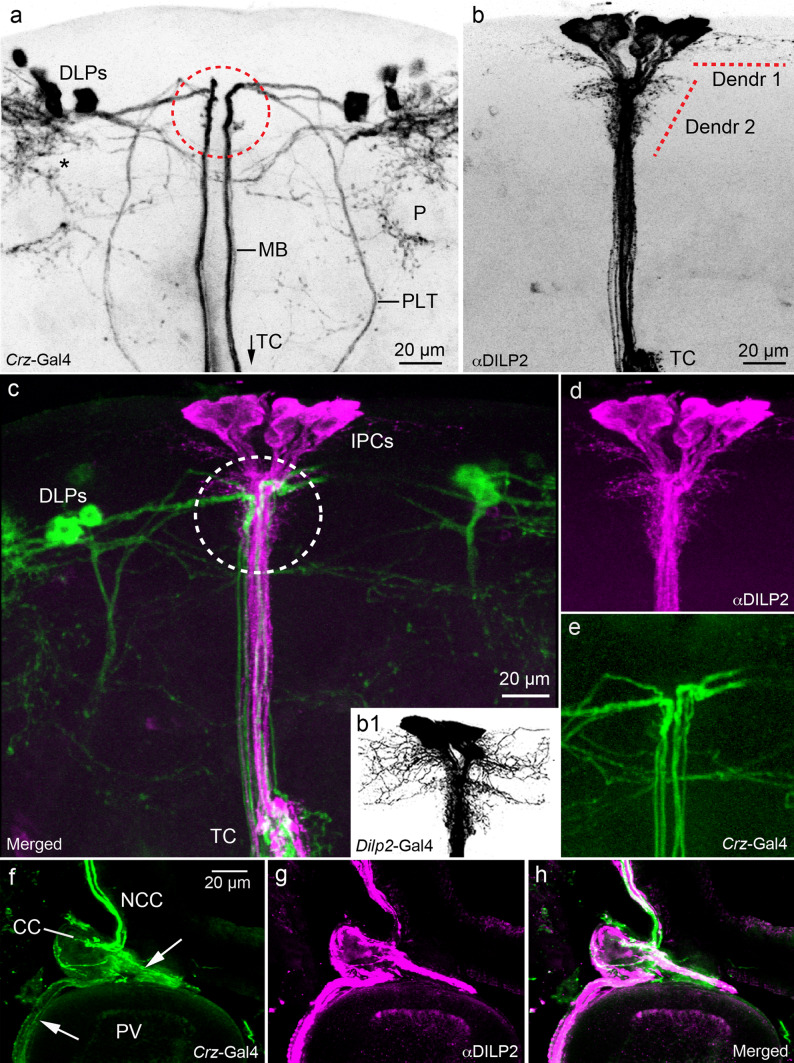
Spatial relations between corazonin/sNPF-expressing DLPs and DILP-producing IPCs in the Drosophila brain. a Morphological details of DLPs, a confocal stack of images of Crz-Gal4 expressing DLPs (inverted in Photoshop to increase contrast). Note the two major axon tracts from DLPs running ventrally towards the tritocerebrum (TC more ventrally, see c), the median (MB) and lateral (PLT) tracts. The DLPs arborize also in the dorsal lateral protocerebrum (asterisk) and around the mushroom body peduncle (P). The area indicated by a red circle corresponds to the Dendr 2 area in Fig 2b. b Details of DILP2 immunolabeled IPCs. Branches are seen in two regions of the pars intercerebralis (Dendr 1 and 2) and in the TC (only partly seen here). The bona fide dendrites of IPCs have not been identified, but could be among the pars intercerebralis branches. b1 Note that when using a Dilp2-Gal4 driver to display these Dendr 1 and 2 branches instead of DILP2 antiserum, they appear much more extensive (inverted image). c–e Double marking of the DLPs (green) and IPCs (magenta) to reveal superposition of some of their processes in the pars intercerebralis (circled area in c). See also S Fig. 2 for further details of superposition of DLP and IPC branches in the brain. f–h The axons of the DLPs (green) and IPCs (magenta) run via the corpora cardiaca (CC) nerves (NCC) into the CC and further into nerves (arrows) that supply axon terminations of the proventriculus (PV) foregut and crop duct (not shown). This is another site where the DLPs might regulate IPCs by corazonin and sNPF release