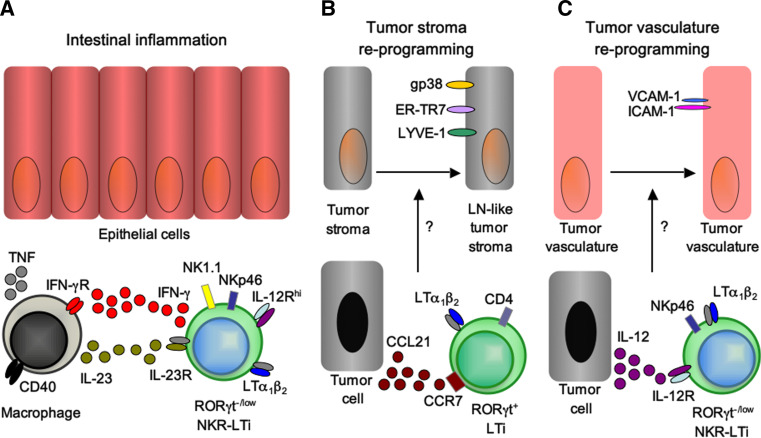
Fig. 3.
LTi lineage subsets play important roles during inflammatory bowel disease and for tumor immunity. a RORγt−/low NKR-LTi cells induce innate CD40 colitis. Activation of lamina propria myeloid cells via CD40-ligation induces IL-23 secretion. IL-23 activates RORγt−/low NKR-LTi cells for the production of IFN-γ [19, 30, 115]. IFN-γ further activates myeloid cells resulting in secretion of large amounts of TNF that may mediate damage of intestinal epithelial cells. b LTi cells reprogram tumor stroma leading to tolerance against the tumor. Tumor cells secreting high levels of CCL21 attract RORγt+ LTi cells via CCR7 to the tumor. RORγt+ LTi cells reprogram the tumor stroma into a lymph node-like phenotype [125]. Lymph node-like tumor stroma dampens anti-tumor immunity by favoring the differentiation of regulatory T cells and by generating a tolerogenic microenvironment thereby preventing tumor rejection. c IL-12-stimulated NKR-LTi cells modifiy tumor vasculature leading to tumor clearance. IL-12 activated NKR-LTi cells reprogram the tumor vasculature to express VCAM-1 and ICAM-1, facilitating entry of effector cells into the tumor tissue resulting in efficient rejection of the tumor [130]