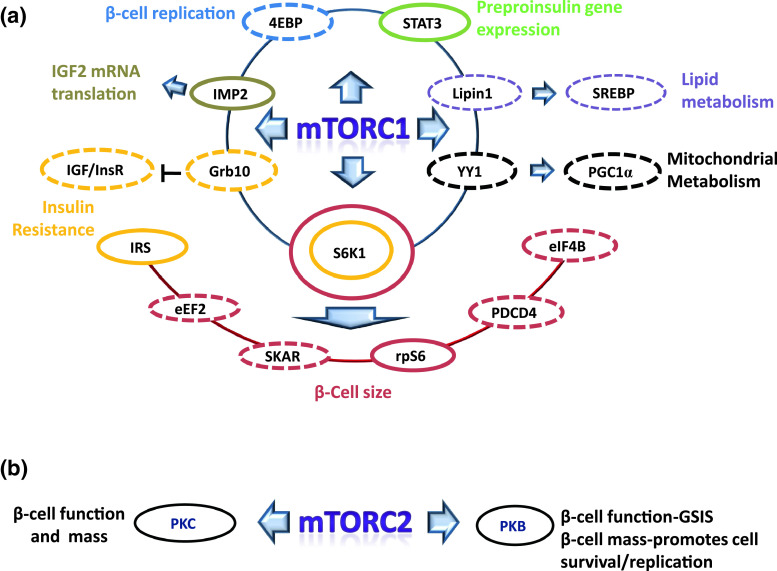
Fig. 3.
Schematic representation of the involvement of protein targets downstream of mTORC1 and 2 in the control of pancreatic β-cell mass and function. Proteins circled in continuous line: function proved in β-cells; Proteins circled in dashed line: function reported in non β-cells, and yet to be studied in β-cells. a Effects of downstream targets of mTORC1 on β-cell function and mass. Using transgenic mouse models it has been shown that S6K1 [ribosomal protein S6 (rpS6) kinase 1] [116] and rpS6 [131] are crucial for the maintenance of β-cell size, although it remains a possibility that other S6K downstream targets, such as SKAR (S6K1 Aly/REF-like target) [126], eEF2 (eukaryotic elongation factor 2) [17, 169], PDCD4 (programmed cell death protein 4) [34] and eIF4B (eukaryotic initiation factor 4B) [125], also contribute to β-cell growth, presumably through their ability of regulating protein synthesis. Insulin resistance can be induced by the inhibition of IRS (insulin receptor substrate) resulted from the over-activation of S6K1 in β-cells [39]. Recently, it has also been reported that newly discovered mTORC1 substrate Grb10 (growth factor receptor-bound protein 10) negatively regulates insulin and IGF (insulin-like growth factor) signalling through the binding and inhibition of InsR (insulin receptor) and IGFR (IGF receptor) [70, 182], which may also contribute to insulin resistance. mTORC1-stimulated fat accumulation is driven by the activation of SREBP (sterol regulatory element-binding protein) [98, 145, 146] through the nuclear import of lipin1 [119]. It has been demonstrated in β-cells that mTORC1 directly phosphorylates IMP2 [insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2) mRNA binding protein] to promote IGF2 mRNA translation [31], and leptin-induced activation of STAT3 (signal transducers and activator 3) suppresses preproinsulin gene expression [96]. Furthermore, it can also be speculated that 4EBP [eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) binding proteins] controls β-cell proliferation, while YY1 (Ying Yang 1) and PGC1α (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-α) [30] may play roles in β-cell mitochondrial metabolism. Circle colours represent: dark red β-cell size; yellow insulin resistance; black mitochondrial metabolism; tan IGF2 mRNA translation; blue β-cell replication; light green preproinsulin gene expression; purple lipid metabolism. b Downstream of mTORC2. Gu et al. [59] have demonstrated that mTORC2 is important in β-cell replication. In addition, mTORC2 is essential for the maintenance of β-cell viability and GSIS (Barlow AD, Xie J and Herbert TP, unpulished data). mTORC2 also controls the folding and protein stability of PKCα (protein kinase C α), PKCβ and PKCε [42, 75], which are known to play important roles in β-cell function and survival [13, 140]