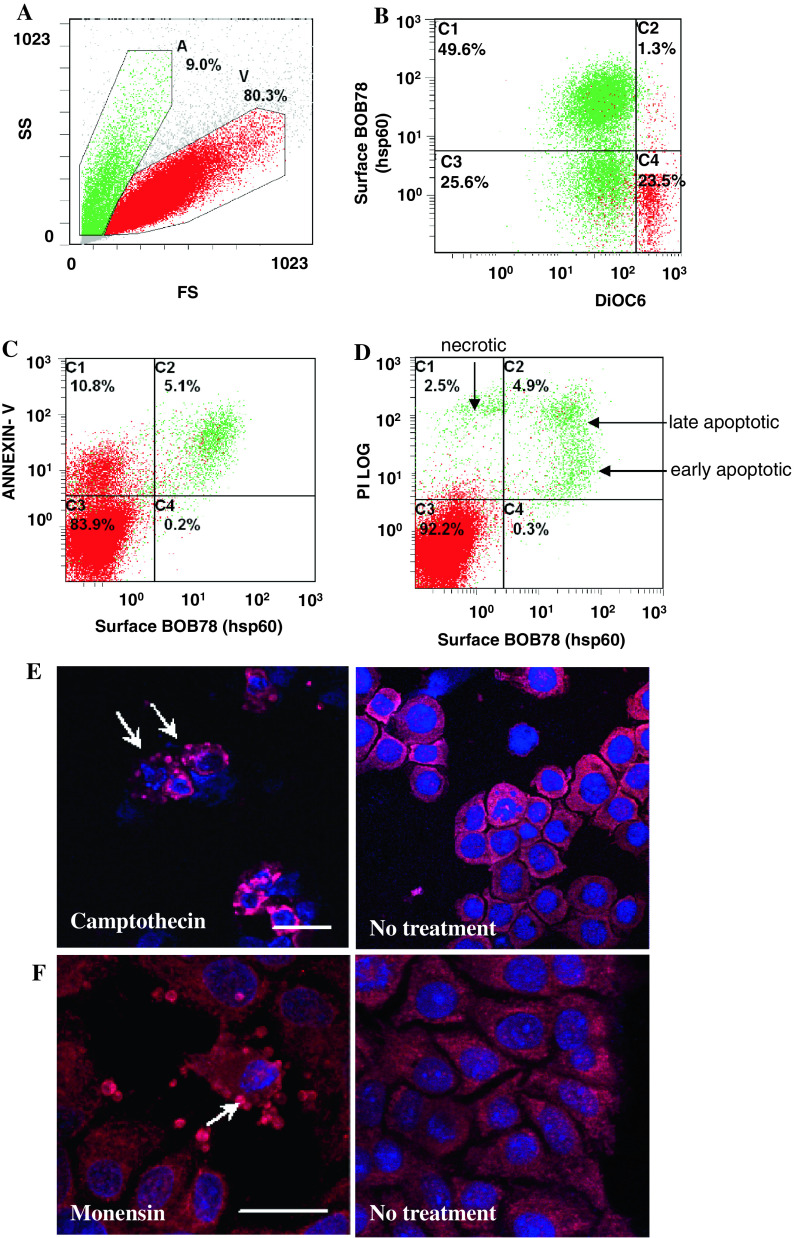
Fig. 3.
Hsp60 is expressed on the surface of cells from early to late apoptosis. Human leukaemic THP-1 cells were treated with 3 μM camptothecin for 6 h and analysed by flow cytometry. The cells were costained with BOB78 antibody (detected with anti-mouse FITC) and PI, DiOC6 or annexin V. PtdSer exposure on the cell membrane was detected by staining with PE-conjugated annexin V. a Camptothecin-treated THP-1 cells were separated by size by flow cytometry. Apoptotic cells (green, A) are smaller than viable cells (red, V). b Hsp60 was detected using BOB78 antibody by PE-conjugated anti-mouse secondary antibody. A significant proportion of cells which have lost the mitochondrial transmembrane potential, reflected by reduced DiOC6 green fluorescence, express Hsp60 on the surface. Surface expression of Hsp60 is therefore an event which follows loss of mitochondrial transmembrane potential, a key event in the initiation of apoptosis. c Hsp60 is coexpressed with PtdSer on the surface of cell membranes, indicating that Hsp60 surface exposure occurs early in apoptosis. d PI staining was performed to assess membrane permeability. Apoptotic cells express Hsp60 on the surface. Viable cells [59] exclude PI and do not express Hsp60. Apoptotic cells, early or late, express Hsp60. Hsp60 expression in necrotic cells is low as these cells lose intracellular Hsp60 expression on membrane lysis. e, f Hsp60 localizes predominantly to the membranes and blebs (arrows) of (e) apoptotic THP-1 cells treated with 3 μM camptothecin for 6 h (bar 15 μm) and (f) human hepatoma HUH-7 cells treated with 25 μM monensin for 6 h (bar 25 μm). Untreated live cells do not exhibit these Hsp60-rich blebs. Nuclear staining was effected with TOPRO-3 (blue fluorescence). Naked nuclear material probably results from lysis of late apoptotic or necrotic cells