Fig. 5.
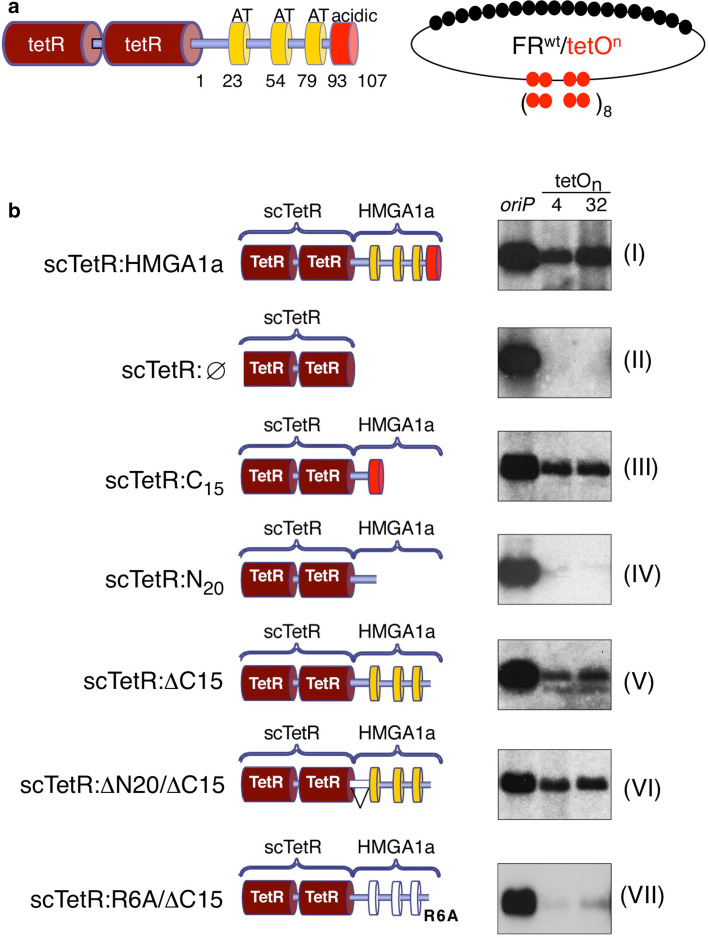
AT-hooks and C-terminal domain of HMGA1a contribute to replication competence of HMGA1a. a Schematics of the single-chain tet-repressor HMGA1a fusion protein (scTetR:HMGA1a, left). Indicated are the single-chain dimer (dark red), the AT-hook domains (yellow boxes) and the acidic domain (red box). A scheme of the reporter plasmids FRwttetO4 and FRwttetO32 is shown for clarity. The 6RA/ΔC15 mutant lacks the last 15 amino acid residues and carries point mutations changing the six arginines of the three AT-hook RGRP-motifs to alanines. b Both reporter constructs were transfected into HEK293 cells expressing EBNA1 and scTetR:HMGA1a (HEK293/EBNA1+/scTetR:HMGA1a+), the indicated mutants of HMGA1a (III–VII), or scTetR only (II). Southern blot analysis was used to visualize extrachromosomally maintained and replicated plasmid DNA using the prokaryotic backbone as plasmid-specific probe. The oriP plasmid was used as a positive experimental control for EBNA1, scTetR:HMGA1a (I) and scTetR:Ø (II) as positive and negative controls, respectively. One representative result out of three or more independent experiments is shown