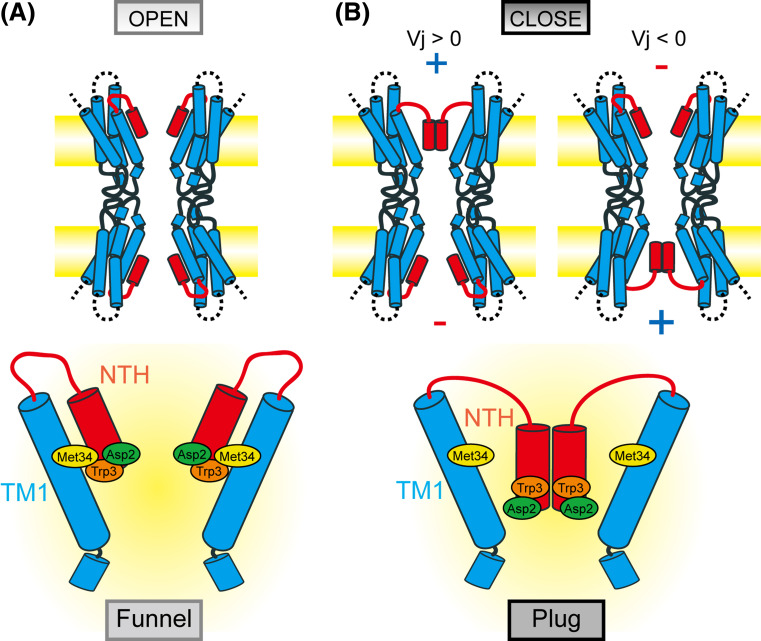
Fig. 9.
Plug gating model for transjunctional voltage-dependent gating of the Cx26 gap junction channel. When there is no difference in membrane voltages between two neighboring cells (a), NTHs form the pore funnel and attach to TM1 by hydrophobic interactions. When there is a difference in membrane voltages between two cells (b), the positive electric field pulls up Asp2, which is exposed to the pore, in the cytoplasmic direction, releasing NTHs from TM1. Once released, NTHs will assemble on the top of the pore and form a so-called “plug” structure