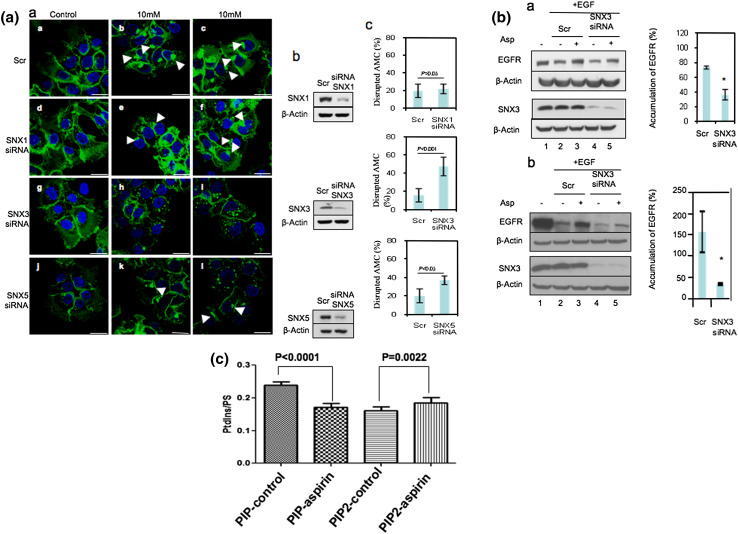
Fig. 6.
Aspirin-induced accumulation of EGFR in the sorting endosomes is dependent on the expression of SNX3. a Cells transfected with control (Scr) or SNX-specific siRNA duplexes for 36 h were serum starved for 12 h prior to incubation with 2 μg/ml of Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated EGF on ice for 1 h. Thereafter, cells were treated with varying concentrations of aspirin for 2 h. a Image of confocal microscope, scale bars 25 μm. Arrows indicate the AMC. c Amount of AMC-negative cells upon treatment with 10 mM aspirin were counted and normalized to total number of cells. Columns average of normalized values from three independent experiments, bars ±SD. Results with significant statistical difference from Scr, *p < 0.05. b WB was performed to assess knockdown efficiency. b Serum-starved siRNA-transfected A-431 cells were treated with 100 nM of EGF and 10 μg/ml of cycloheximide, in the absence (−) or presence (+) of 5 mM aspirin for 6 h prior to WB analysis (a). A similar experiment was done in HeLa cells (b) using 40 nM EGF, 5 mM aspirin, and 2 h incubation. The change in EGFR expression in siRNA-treated samples upon treatment with aspirin was normalized to untreated sample (right). Columns average values from two independent experiments, bars ±SD. Results with significant statistical difference from Scr: *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.001. c Lipid ion chromatography analysis showed that aspirin did not elevate synthesis of total PIP lipid on membranes