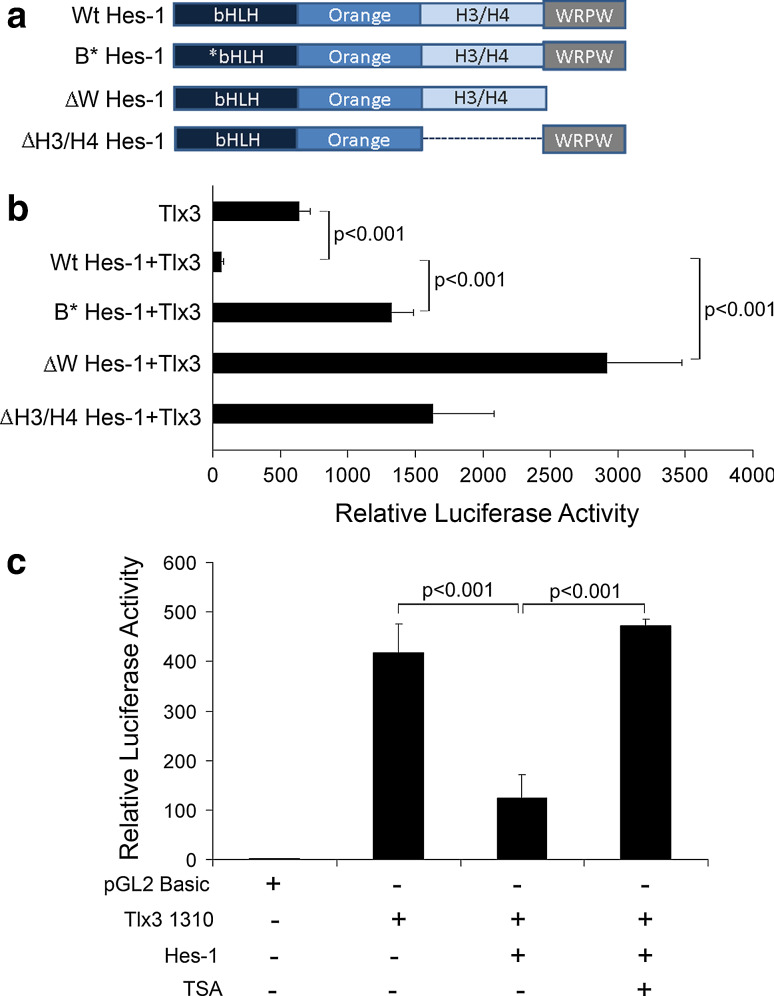
Fig. 5.
WRPW domain mediated-protein interaction along with DNA- binding and histone deacetylase activity is involved in regulation of Tlx3 promoter: a Schematic representation of different functional domains of Wt type Hes-1 and different truncated/mutated Hes-1 proteins used in this study. B*Hes-1 represents basic domain-mutated Hes-1 and thus is unable to bind target DNA. However, all of the other domains are intact so that it can interact with other proteins and is able to recruit co-repressor proteins and can dimerize with other bHLH factors. ∆W Hes-1 represents WRPW domain truncation with deletion of extreme C-terminal four amino acids. ∆W Hes-1 is able to carry out all functions of Hes-1 except co-repressor recruitment. ∆H3/H4 Hes-1 indicates H3/H4 domain truncated Hes-1, where protein–protein interactions may be affected. b Luciferase activity was measured with co-transfection of the above-mentioned Hes-1 constructs along with pTlx3 1310-Luc to study the contribution of different functional domains of Hes-1 in Tlx3 promoter regulation. The Wt type Hes-1 significantly repressed (p < 0.001) Tlx3 promoter activity, whereas B*Hes-1 significantly reduced (p < 0.001) the repression compared to Wt type, indicating a function role of DNA binding in Tlx3 promoter regulation. Again, ∆W Hes-1 with WRPW domain truncation showed a significant activation/de-repression (p < 0.001) of the promoter, indicating an active co-repressor recruitment role in Tlx3 promoter regulation. ∆H3/H4 domain truncated Hes-1 also did not show any repression indicating functional protein interactions even with co-repressors in Hes-1-mediated repression. c Treatment with deacetylase inhibitor, Trichostatin A (TSA) resulted in the abolishment of inhibition caused by Hes-1. These results indicated that histone deacetylase activity is one of the mechanisms through which Hes-1 represses the Tlx3 promoter