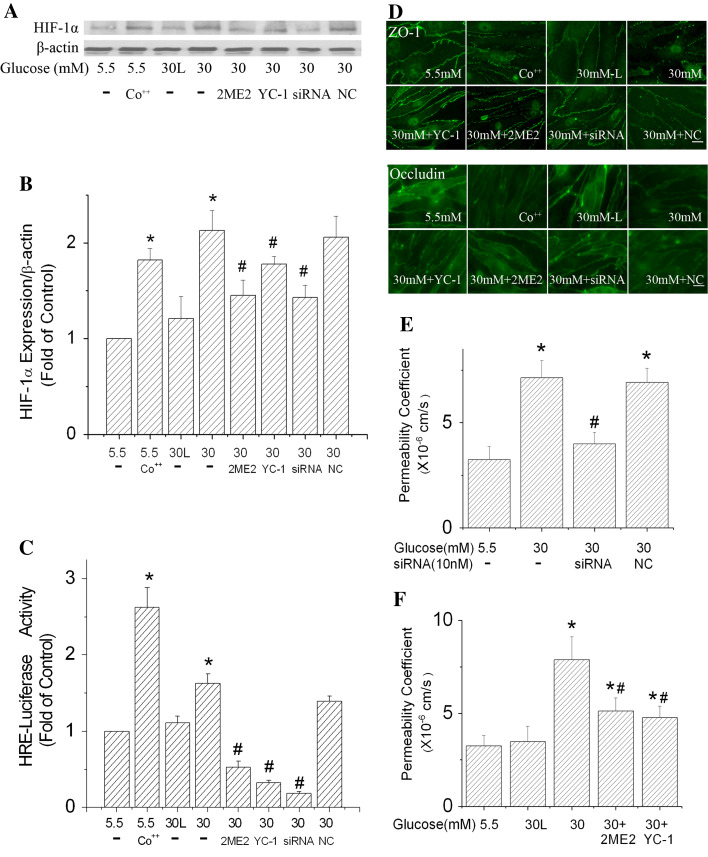
Fig. 5.
Effects of HIF-1α inhibition on the paracellular permeability of b.End3 cells exposed to high glucose. HIF-1α-specific siRNA (siRNA) and negative control siRNA (NC) transfection was conducted every 2 days. HIF-1α inhibitors (10 μM YC-1, or 10 μM 2ME2) were added to the culture medium 2 h before the onset of high glucose (30 mM) treatments and were added with each medium change (every 2 days). For Co++ experiments, 100 μM CoCl2 was added to culture medium (5.5 mM glucose) 24 h before the assays. Cells treated with 30 mM l-glucose (30 L) in the presence of 5.5 mM d-glucose served as an osmotic control. a Representative Western blots of HIF-1α with β-actin as a protein-loading control. b HIF-1α protein expression summarized from three independent experiments. c Inhibiting HIF-1α reduced the increase of HRE-luciferase activity in b.End3 cells. d Inhibiting HIF-1α improved the local distribution of ZO-1 and occludin. Scale bar 22 μm. e Suppression of HIF-1α expression by siRNA reduced the effect of high glucose on b.End3 paracellular permeability. f HIF-1α inhibitors, 2ME2 and YC-1, ameliorated the increased paracellular permeability caused by 30 mM glucose. Values in b and c were normalized to β-actin and control (5.5 mM glucose). Values are means ± SEM, n = 3. *p < 0.05 versus control (5.5 mM glucose). # p < 0.05 versus 30 mM glucose