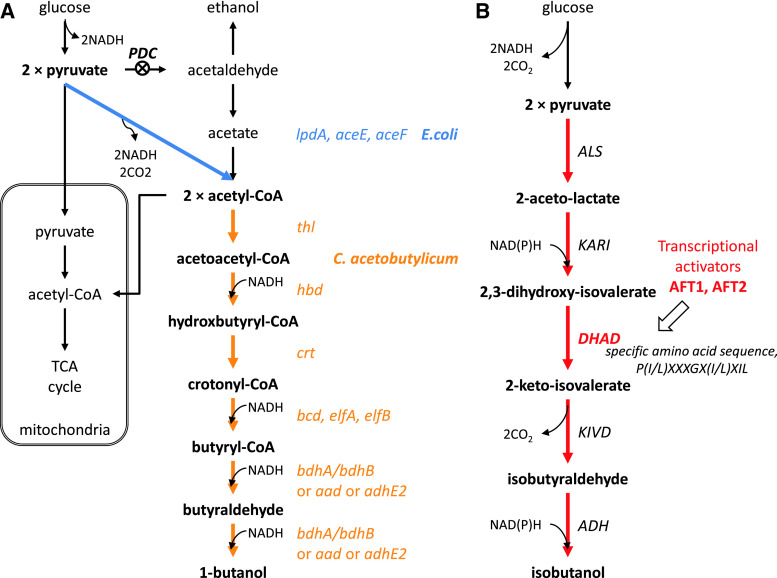
Fig. 5.
Illustration of Gevo’s strategies for n-butanol and isobutanol production in the cytosol [90, 91, 105]. a n-butanol production was attempted by amplification of heterologous genes such as the pyruvate dehydrogenase multienzyme complex (lpdA, aceE, aceF) from E. coli for increasing the cytosolic acetyl-CoA pool, and the genes in butanol synthetic pathway from Clostridia species. Moreover, the activity of pyruvate decarboxylase (PDC) was reduced. b Isobutanol was produced in the cytosol to avoid cofactor balancing in the mitochondria; all the genes in isobutanol pathway were over-expressed in cytosol. Especially, dihydroxyacid dehydratases (DHAD) from Lactococcus lactis and Neurospora crassa were used, which had specific amino sequence, P(I/L)XXXGX(I/L)XIL. Also, the transcriptional activators AFT1/AFT2 were over-expressed to increase DHAD activity