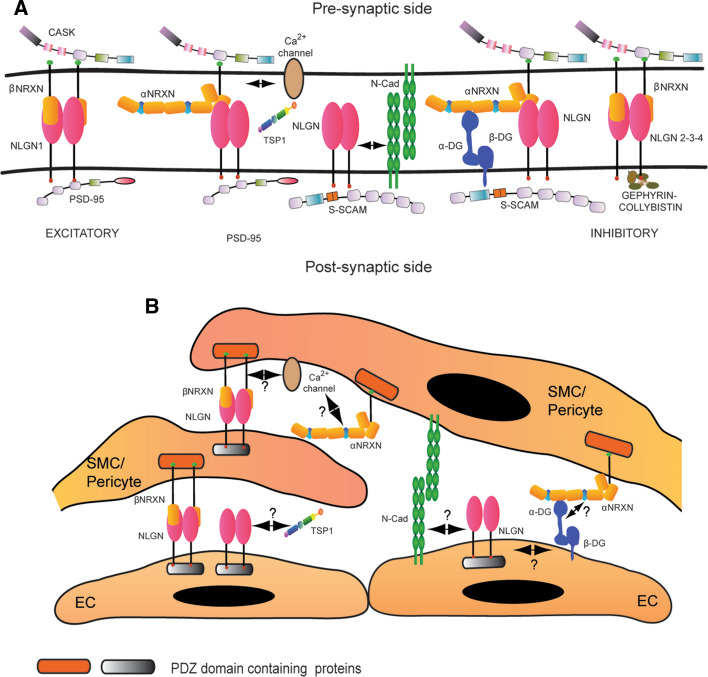
Fig. 3.
Molecular interactions of Neurexin and Neuroligin. a General summary of the main biochemical interactions described for Neurexin and Neuroligin in the central nervous system. Neurexin and Neuroligin localize at the pre- and post-synaptic side, respectively, and two β-Neurexin molecules bind a Neuroligin dimer. Neuroligin 1 is enriched at the excitatory synapses, where it binds PSD-95. Neuroligin 2 and 3 are preferentially expressed at inhibitory synapses, where the post-synaptic scaffold is nucleated by Gephyrin and Collybistin. Another PDZ-domain protein that interacts with Neuroligin is S-SCAM, which mediates the binding with N-Cadherin (N-Cad) and Distroglycan (DG). Thrombospondin 1 (TSP1) has been recently reported as a new interactor for Neuroligin 1. CASK is the only intracellular binding partner identified for Neurexin and, through the recruitment of other adaptor proteins, it creates a bridge with Ca2+channels. The three-dimensional molecular arrangement of Neurexins and Neuroligins as well as the identity of the other interacting partners at the synapse were derived from references [58, 120–122]. The double arrow represents the functional interaction between Neuroligin 1 and N-cadherin [64] and between α-Neurexins and voltage dependent calcium channels (VDCC) [52]. b Hypothetical reconstruction of the Neurexin and Neuroligin molecular partners in blood vessels. Very little is known about the biochemical network around Neurexin and Neuroligin in the vascular system. We demonstrated that Neuroligin is widely expressed in blood vessels, while Neurexin is preferentially restricted to mural cells. In the vascular system, the β isoform of Neurexin preferentially binds Neuroligin. Moreover, a link between Neurexin and Ca2+channels might also exist in blood vessels. Considering the vascular expression of several described Neurexin and Neuroligin partners, we propose a potential scenario of molecular interactions that may involve these proteins in blood vessels. Question marks indicate the hypothetical interactions. Finally, since their identity needs to be confirmed, the intracellular partners of Neurexin and Neuroligin are generally indicated as PDZ domain containing proteins and labeled with a different color code because of their are likely part of respectively “pre- and post-synaptic” families