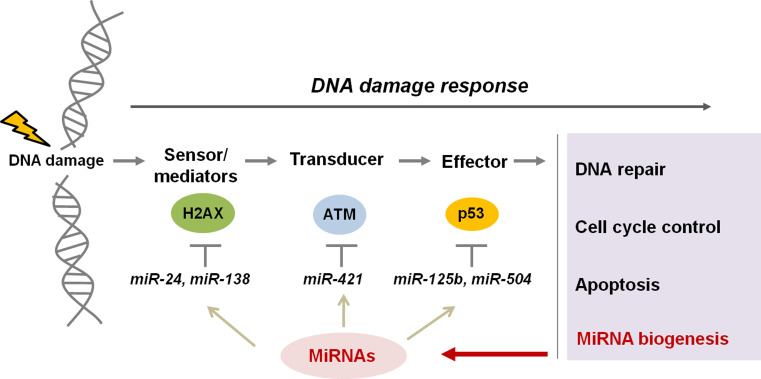
Fig. 1.
Crosstalk between the DNA damage response pathway and miRNAs. The DNA damage response (DDR) pathway is comprised of a number of different proteins that function to coordinate the repair of DNA damage and preserve genomic integrity. These proteins are classified as either sensors, transducers, or effectors, depending on their specific function. Recent studies have shown that miRNAs may play a regulatory role in the DDR by targeting and modulating the expression of genes involved in the DDR. For example, H2AX is targeted by miR-24 and miR-138, and ATM is controlled by miR-421. P53, a critical effector protein in the DDR pathway, is targeted by miR-125b and miR-504. There is also data to suggest that the DDR is also involved in the regulation of miRNA biogenesis