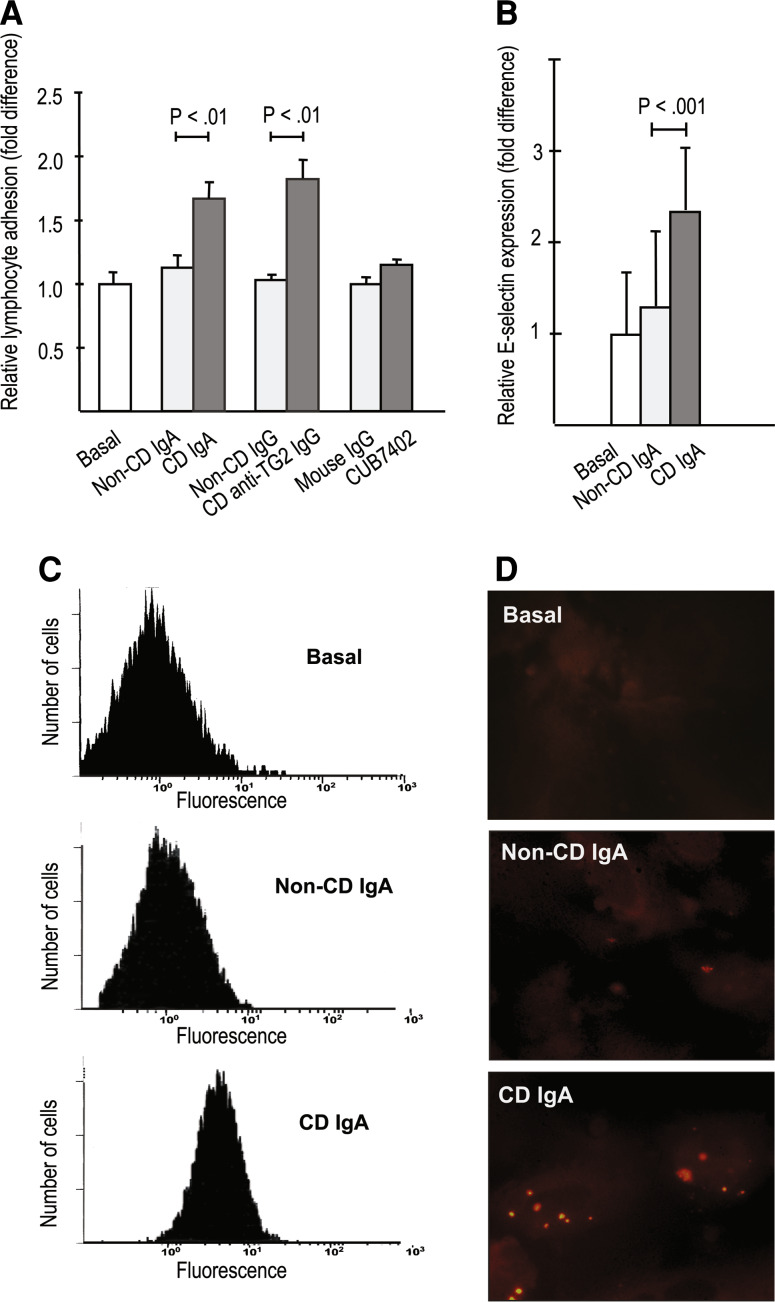
Fig. 2.
Lymphocyte adhesion on endothelial cells. a Lymphocytes adhered more prominently to endothelial monolayer treated with celiac disease (CD) patient-derived antibodies [CD total IgA and CD anti-transglutaminase 2 (TG2)-specific IgG] when compared to control (non-CD) antibodies. Commercially available anti-TG2 antibody CUB7402 had no effect. b CD IgA increased the expression of the endothelial adhesion molecule E-selectin significantly when compared to non-CD IgA (b) analysed by flow cytometry (b, c) and by immunofluorescent labelling (d, in red). Experiments were performed in duplicate and repeated at least three times. Bars represent mean values and error bars standard error of means. Only significant differences (P < .05) between the relevant antibody groups are depicted