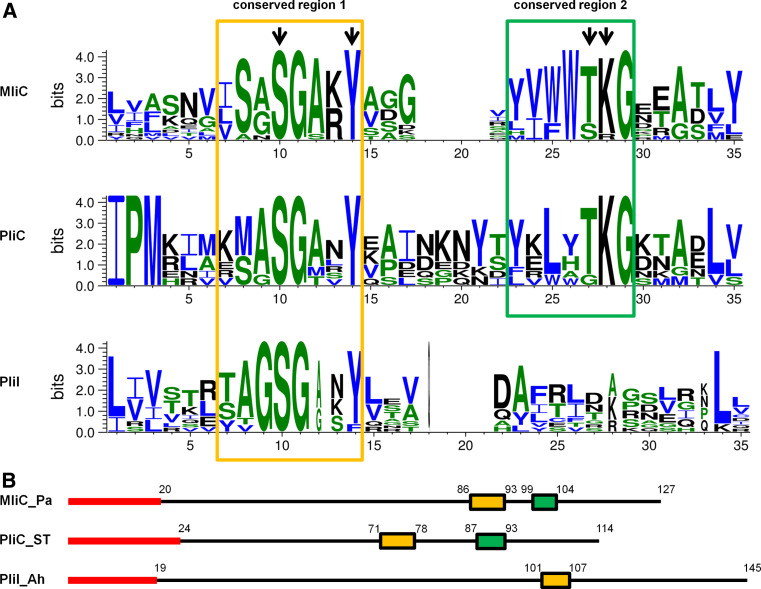
Fig. 5.
Representation of the common conserved regions in MliC, PliC and PliI. a Sequence logos built with weblogo 3.0 [48], showing conserved motifs detected using GLAM2 [42], in a set of 13 MliC, 10 PliI and 7 PliC homologues. Homologues were obtained by tblastn search in the NCBI database, starting with MliC from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1, PliC from Salmonella Typhimurium LT2 and PliI from Aeromonas hydrophila ATCC7966, and retaining one sequence for every different genus harboring a homologue with an E-value of at least 8.0 e−4. Signal peptides as predicted by Signal 3.0 [25] or Dolop [49, 50] were omitted from the motif search. Conserved residues shown to be involved in the interaction of P. aeruginosa MliC and HEWL by Yum et al. [16] are indicated by black arrows. Amino acids are colored by hydrophobicity: hydrophobic, blue; neutral, green; hydrophilic, black. b Schematic representation of the distribution the conserved regions 1 (orange) and 2 (green) along the protein sequence of MliC (Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1), PliC (Salmonella Typhimurium LT2) and PliI (Aeromonas hydrophila ATCC7966), respectively. The signal peptides are shown in red, and numbers represent amino acid positions