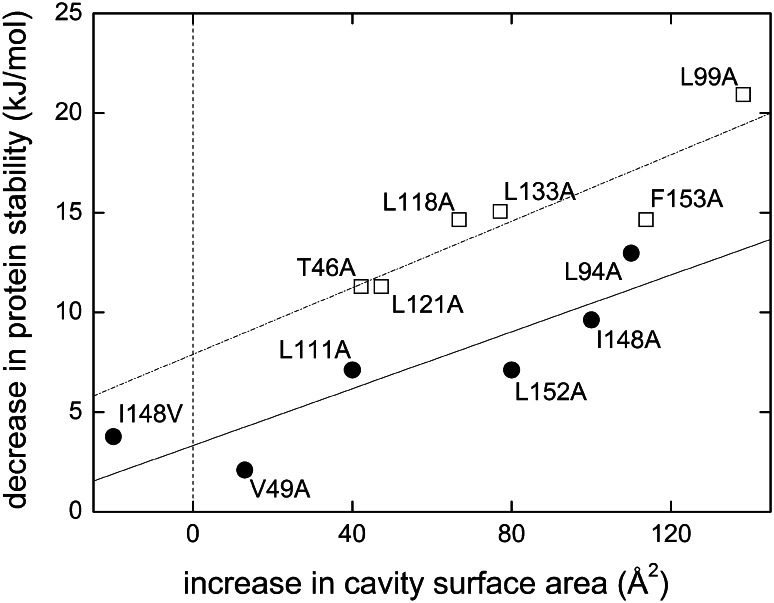
Fig. 7.
Dependence of protein stability on cavity surface area in water-soluble and membrane proteins. Experimental data for T4 lysozyme (open squares, taken from [80]) and bacteriorhodopsin (filled circles, [79]) as well as linear regressions (dash-dotted and solid lines, respectively). The stabilities of both proteins decreased in a roughly linear fashion with an increase in cavity surface area caused by the large-to-small amino acid substitutions indicated in the figure. Similar slopes observed for the two proteins suggest that van der Waals forces contribute equally to the stabilities of water-soluble and membrane proteins. The y-axis intercepts are different because of the greater contribution of the hydrophobic effect in thermal unfolding of T4 lysozyme as compared with SDS denaturation of bacteriorhodopsin. Figure adapted with permission from [79]. Copyright 2009 American Chemical Society