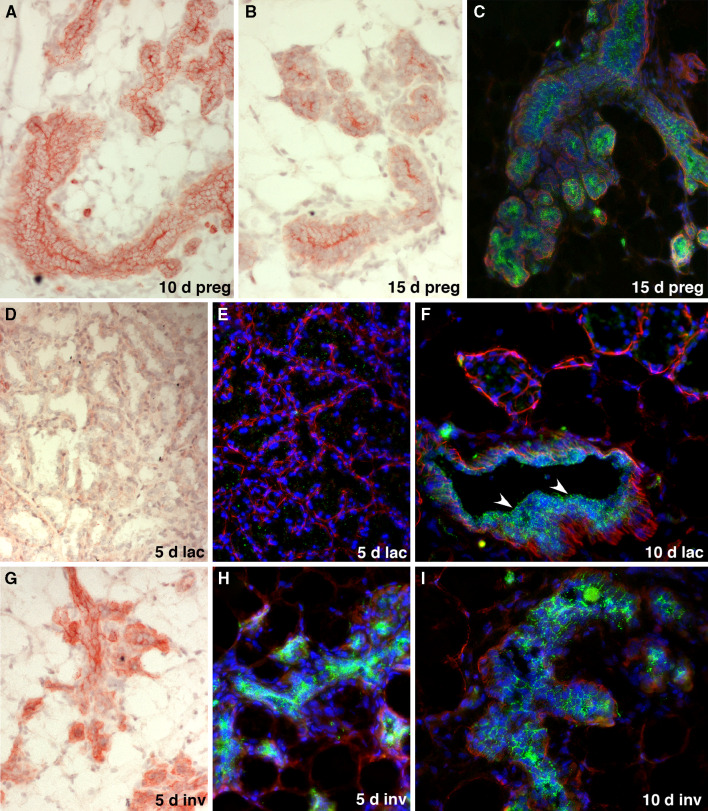
Fig. 3.
Expression of CD24 in the murine mammary gland during pregnancy, lactation and involution. a–c Expression of CD24 in the mammary epithelium of mice pregnant for 10 days (a) and 15 days (b, c) detected by red Fuchsin chromogen staining (a, b) or as green fluorescence (c). Staining for smooth muscle actin (red fluorescence) and DAPI staining of nuclei (blue fluorescence) was also performed in c. Note the reduced CD24 staining in the alveolar epithelial cells, with the exception of the cell surfaces forming the closed lumen of the alveoli. d–f Expression of CD24 in the mammary epithelium of mice that had been lactating for 5 days (d, e) and 10 days (f), detected by red Fuchsin chromogen staining (d) or green fluorescence, together with smooth muscle actin (red fluorescence) and blue DAPI staining of nuclei (e, f). Note the virtual absence of CD24 expression in the alveoli. The arrowheads in f indicate retention of robust CD24 staining in milk collecting ducts. g–i Expression of CD24 in the mammary epithelium of post-lactating mice, 5 days (g, h) and 10 days (i) after the weaning of their pups. CD24 expression was detected by red Fuchsin chromogen staining (g) or by green immunofluorescence, together with smooth muscle actin (red fluorescence) and blue DAPI staining of nuclei (h, i). Note the increased CD24 expression in the remodeled epithelium that rapidly returns to a CD24 expression pattern typical of pre-pregnant ducts