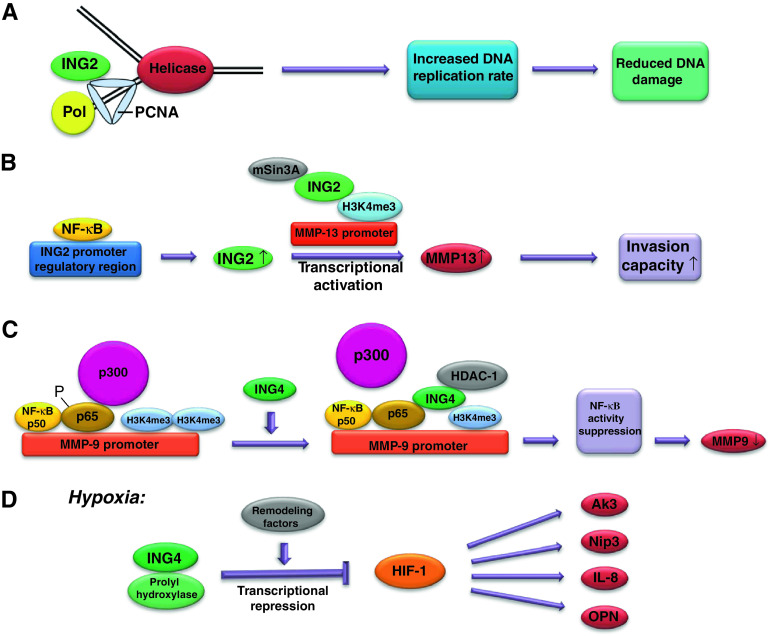
Fig. 1.
Potential mechanisms for ING transcriptional regulation of genes involved in cancer progression. a ING2 interacts with PCNA during DNA replication, allowing normal cell proliferation to maintain genomic stability. b In colon cancer, NF-κB binds to the ING2 promoter regulatory region, increasing the expression of ING2. ING2 recruits mSin3a to the MMP-13 promoter and binds to H3K4me3 resulting in MMP-13 transcriptional activation. c ING4 binds to NF-κB at the promoter of NF-κB-regulated genes and suppresses NF-κB activity via reducing H3K4me3 and inhibiting NF-κB p65 phosphorylation. ING4 decreases p65–p300 interaction in favor of HDAC-1 recruitment. d During hypoxia, ING4 interacts with the prolyl hydroxylase and recruits chromatin-remodeling factors to HIF target gene promoters, suppressing HIF-1-regulated gene expression