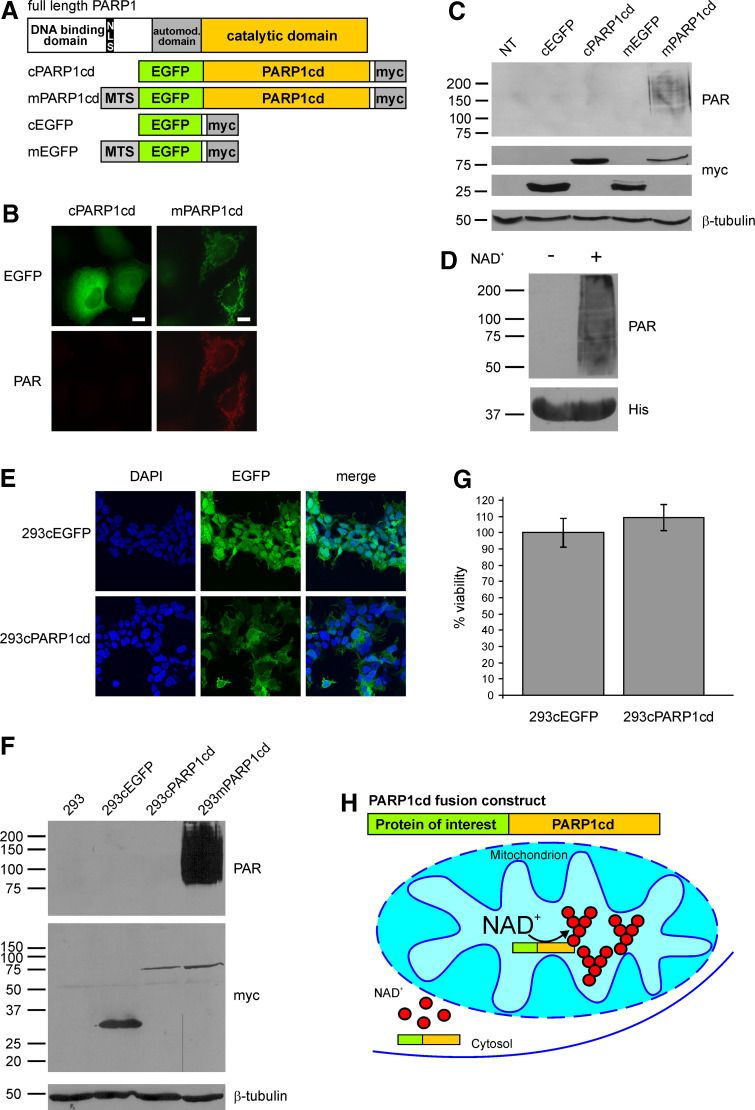
Fig. 1.
Mitochondrial, but not cytosolic overexpression of PARP1cd results in immunodetectable PAR accumulation. a Molecular architecture of poly-ADP-ribose polymerase 1 and the generated PARP1cd and EGFP fusion constructs. MTS Mitochondrial targeting sequence, NLS nuclear localization signal. b Fluorescence micrographs of HeLa S3 cells subjected to PAR immunocytochemistry 24 h after transient transfection with vectors encoding cytosolic or mitochondrial EGFP-PARP1cd (cPARP1cd and mPARP1cd). Protein expression was monitored by the intrinsic fluorescence of the EGFP portion of the constructs. Bar 10 μm. c PAR immunoblot analysis of lysates from HeLa S3 cells expressing cPARP1cd or mPARP1cd or the respective constructs lacking the PARP1cd portion (cEGFP and mEGFP). Overexpression of the proteins was detected by the C-terminal myc-tag. As observed in (b), PAR formation was only detected in cells expressing mPARP1cd. Loading control: β-tubulin. d Addition of NAD+ (1 mM) to bacterially expressed human PARP1cd (amino acids 652–1014) led to automodification of the protein as visualized by PAR immunoblot analysis. The bottom part shows the immunodetection of the protein’s 6xHis-tag. e Stably transfected 293 cells expressing cytosolic EGFP (293cEGFP) or cytosolic EGFP-PARP1cd (293cPARP1cd). Protein expression as monitored by the intrinsic fluorescence of the EGFP portion of the constructs is detectable in all cells. f Immunoblot analyses of lysates from parental and stably transfected 293 cell lines. Expression of cEGFP, cPARP1cd and mPARP1cd was detected by the C-terminal myc epitope. Mitochondrial and cytosolic PARP1cd fusion proteins were expressed at similar levels. PAR immunoblot analysis using 10H antibody revealed detectable PAR formation only in cells expressing mitochondrial PARP1cd. Loading control: β-tubulin. g Constitutive expression of cPARP1cd does not affect cell viability. Cells were seeded into 96-well plates and the viability was determined by MTT assay. Viability of 293cPARP1cd was related to control 293cEGFP cells set to 100%. Data are shown as mean ± SE of four experiments, each performed in triplicate. h Schematic representation of the observed differences in PAR accumulation mediated by targeted overexpression of PARP1cd fusion proteins. Cytosolic PARP1cd does not give rise to immunodetectable PAR. NAD and ADP-ribose are not recognized by the PAR-specific antibodies. The presence of PARP1cd within mitochondria leads to extensive PAR formation