Fig. 1.
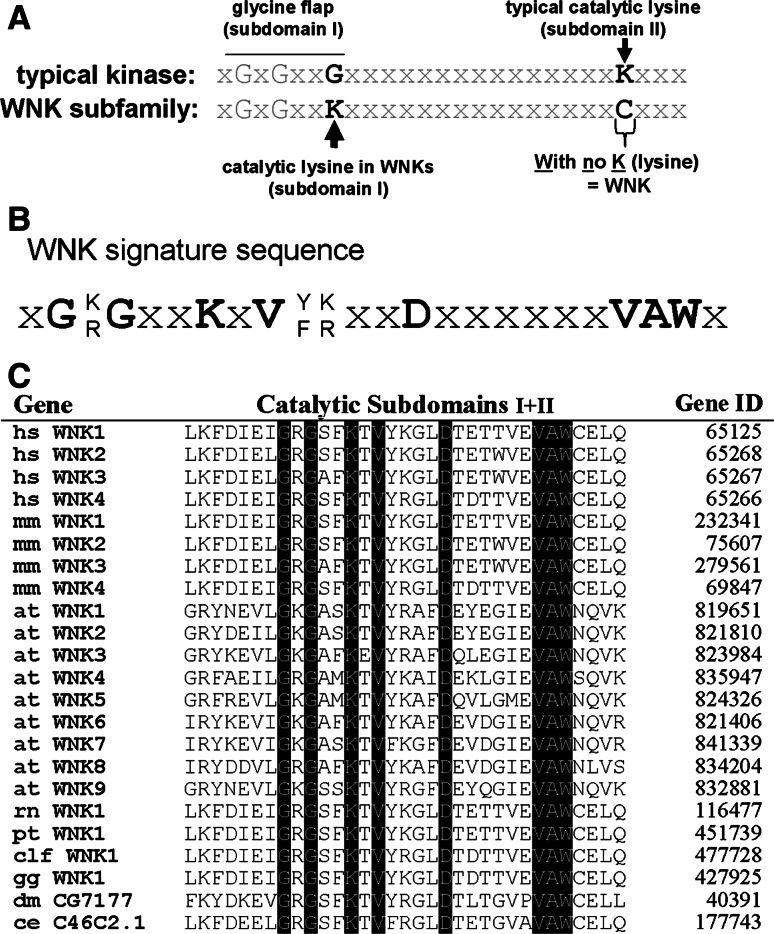
Sequence features of the WNK subfamily of protein kinases. a Comparison of the sequence in subdomains I and II of the catalytic domain between a typical protein kinase and the WNK domain. A conserved lysine in subdomain II, which binds ATP, is absent in WNK kinases and functionally substituted by another lysine located in subdomain I [5, 7], as indicated. b The invariant WNK signature sequence identified from the sequence alignment shown in (c). c Alignment of subdomains I and II of the catalytic domains of WNK kinases from various species. Species abbreviations are: hs Homo sapiens, mm Mus musculus, at Arabidopsis thaliana, rn Rattus norvegicus, pt Pan troglodytes, clf Canis lupus familiaris, gg Gallus gallus, dm Drosophila melanogaster, ce Caenorhabditis elegans (updated from Veríssimo and Jordan 6)