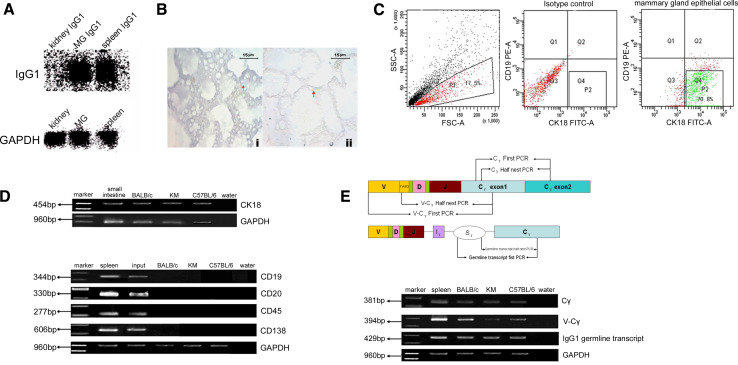
Fig. 2.
Expression of IgG1 heavy chain in mammary gland epithelial cells. a Northern blot analysis. Total RNA from lactating mammary gland, spleen (positive control), and kidney (negative control) were electrophoresed, transferred to nylon membrane, and then probed with a probe to IgG1 heavy chain constant region. The blot was striped and rehybridized with a GAPDH probe (MG mammary gland tissue). b In situ hybridization analysis using antisense (i) or sense (ii) cRNA for heavy chain constant region of IgG1 as a probe. Scale bar 15 μm. c Flow cytometry sorting of the lactating mammary gland epithelial cells by antibodies against CK18 and CD19. The background fluorescence was determined using cells incubated with secondary antibody only (without primary antibody). Cells which were positive for CK18 but negative for CD19 as shown in gate P2 were selected for further analysis. d RT-PCR analysis showed expression of CK18 and lack of expression of CD19, CD20, CD45, and CD138 in the sorted CK18+CD19− cells. Input Cells from mammary gland of lactating mouse without sorting. The small intestine cDNA library was used as a positive control for CK18. The spleen cDNA library was also used as a positive control for CD19, CD20, CD45, and CD138. e PCR analysis showed the expression of IgG1 heavy chain constant and variable regions and IgG1 germline transcripts. V-Cγ The variable region and constant regions of IgG1 heavy chain; Cγ the constant region of IgG1 heavy chain