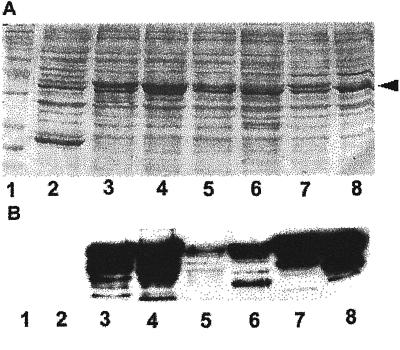
Figure 1.
Western-blotting analysis of GST-Rop fusions. Different Rop-coding sequences were fused to the C terminus of GST and expressed in Escherichia coli as described (Wu et al., 2000). E. coli extracts were separated on a 12% (w/v) SDS PAGE gel, blotted onto a nitrocellulose membrane, and reacted with anti-Rop1Ps antibodies as described (Lin et al., 1996). A, Shows the membrane stained with 0.1% (w/v) Poceau S for loading control of total E. coli proteins. Arrowhead indicates the position of GST-Rop fusion proteins. B, Shows Rop-specific signals detected by the anti-Rop1Ps antibodies. For some lanes, multiple bands were detected as a result of protein degradation. Negative control lane (GST) did not show any signal even after an extended exposure. Lane 1, protein Mr markers; lane 2, GST; lane 3, Arac10; lane 4, Arac8; lane 5, Rop8; lane 6, Rop7; lane 7, Rop6; lane 8, Rop2.