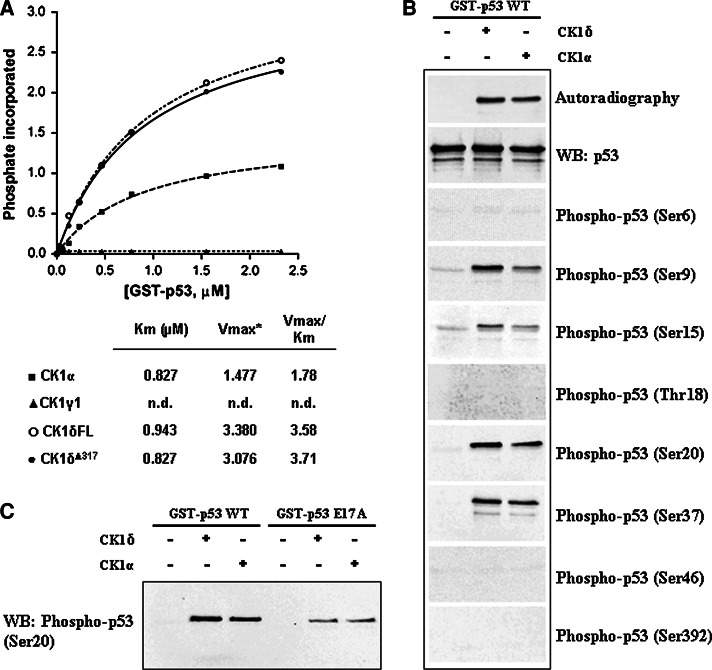
Fig. 5.
Phosphorylation of p53 proteins by CK1 isoforms. a The kinetics of phosphorylation by CK1 isoforms of increasing concentrations of full-length GST-p53 wild-type are illustrated. p53 was subjected to phosphorylation with the indicated CK1 isoforms as described in “Materials and methods”. Of note are the identical kinetics of full-length and truncated (Δ317) CK1δ, this latter sharing 95% identity with the ε isoform. *V max is expressed as picomoles of phosphate transferred per minute per unit of enzyme; n.d. not determined due to undetectable phosphorylation. b Full-length human GST-p53 (1.2 μg) produced in E. coli was phosphorylated by 10 min incubation with either CK1δ or α isoforms and subjected to western immunoblotting analysis with the antibodies indicated on the right. Superimposable kinetics and phosphorylation pattern were obtained replacing GST-p53 with untagged p53 obtained by proteolytically removing of the tag (see “Materials and methods”). c Effect of the Glu17 to Ala mutation on p53 S20 phosphorylation by CK1. Equal amounts (1.2 μg) of full-length p53, either wild-type or E17A mutant, were incubated under the same conditions (see “Materials and methods”) with CK1δ or CK1α. Western immunoblot with the specific phospho-p53 (Ser20) antibody is shown. Densitometric analysis of the anti-phospho-S20 signal shows a remarkable decrease in phosphorylation of the E17A mutant by CK1α (70%) and δ (90%)