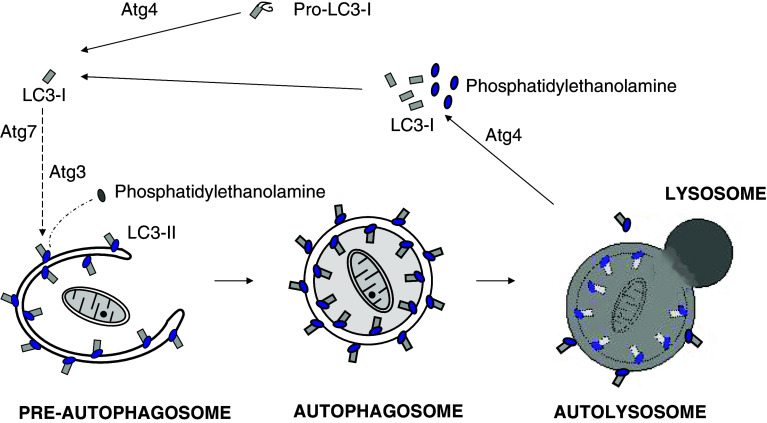
Fig. 6.
Covalent binding of LC3 to phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) is essential for autophagosome formation. In mammalian cells, cytosolic LC3-I (Atg8 in yeast) is synthesized as a precursor (Pro-LC3-I). Immediately after its synthesis, a C-terminal fragment is cleaved by Atg4 to produce LC3-I with an exposed glycine residue that binds covalently to PE on the pre-autophagosome membrane to form LC3-II. In this process, the mammalian homologues of Atg7 and Atg3 work, respectively, as the E1- and E2-like enzymes of the ubiquitination system, and the Atg16L complex probably functions as an E3-like enzyme. Once the autophagosome is formed, LC3-II localizes both at the cytosolic and luminal faces of its double membrane. After fusion of the autophagosome with endosomes/lysosomes to form an autolysosome, the luminal LC3-II is degraded by lysosomal cathepsins, while Atg4 recycles LC3-I and PE from LC3-II on the cytosolic face of the autolysosome membrane