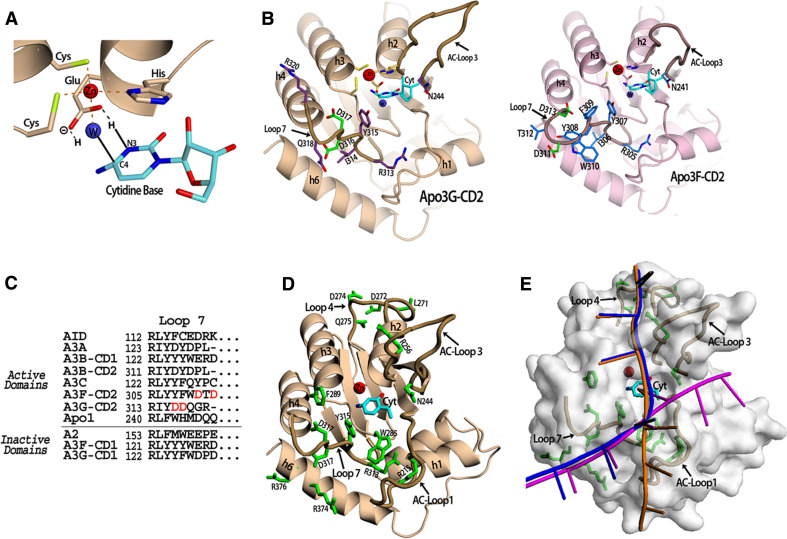
Fig. 2.
APOBEC DNA Binding. a The APOBEC active site containing a cytidine base. The Apo3G-CD2 crystal structure was superimposed with the mouse CDA co-crystal structure with cytidine in the active site (PDB 2fr6) in order to place the cytidine base in this position (shown in cyan). Three residues (2 cysteines and 1 histidine) coordinate the zinc ion (red sphere) along with a water molecule (blue sphere). The conserved glutamate shuffles the protons from the water molecule to the cytidine during the hydrolytic deamination. The proposed mechanism occurs via the glutamate acting to protonate N3 of the cytidine ring by transferring a hydrogen molecule from the water. Next, the activated water molecule (a Zn-hydroxide) attacks the C4 of the cytidine ring resulting in the release of ammonia. b The Apo3G-CD2 structure (PDB 3e1u) which shows the residues on Loop 7 which influence APOBEC substrate specificity. Residues previously shown to be important for Apo3G-CD2 substrate specificity (D316 and D317) are shown in green. Other residues on Loop 7 (shown in purple) may contact the residues neighboring the target cytidine through electrostatic, hydrophobic or base stacking interactions. N244 on AC-Loop 3 is conserved throughout the zinc-dependent deaminase family and has been shown to contact the target base directly (inset). The model of Apo3F-CD2 shows the predicted Loop 7 residues. The SWISS-MODEL homology modeling program was used to generate the model using the Apo3F sequence and the Apo3G-CD2 crystal structure (PDB 3e1u) as a template [106]. Residues D311 and D313 shown in green on Loop 7 have previously been shown to be important in substrate specificity. The conserved N241 which may directly contact the target cytidine is shown on AC-Loop 3. c An alignment of APOBEC proteins showing residues predicted to be in Loop 7. The domains are categorized according to whether they have been shown to be active for deamination activity. d Apo3G-CD2 residues previously reported to be important for DNA binding. The cytidine base is colored cyan and DNA binding residues are colored green. e The proposed Apo3G-CD2 DNA binding models. The target cytidine (cyan) is shown in its proposed position in the active center (see a). The DNA binding model proposed by Holden et al. [1] is shown in magenta. The model proposed by the Chen et al. and Furukawa et al. is shown in orange [3, 4]. A combination of both models is shown in blue